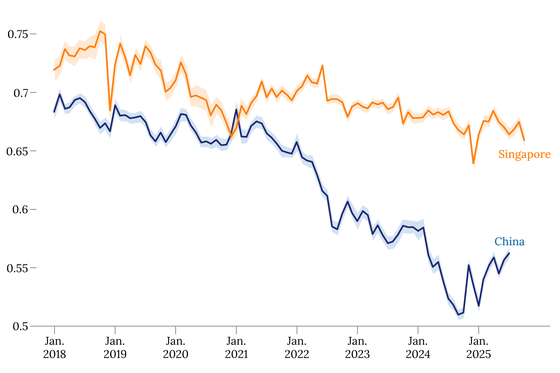
Since the emergence of ChatGPT in late 2022, the global labor market has been gripped by a pervasive concern: the fear of job replacement due to artificial intelligence (AI). This anxiety is particularly pronounced among white-collar workers, with forecasts suggesting that roles in accounting, copywriting, and even coding may become obsolete. However, as we delve into the data three years into this technological transformation, it becomes evident that the impact of AI is not uniform across different economies. A comparative analysis of the labor markets in China and Singapore reveals two distinct trajectories: one characterized by significant worker displacement and another where technology bolsters workforce resilience through integration.
The narrative surrounding AI often highlights its capacity to automate repetitive tasks, thus streamlining operations across various sectors. In China, the rise of generative AI has led to substantial job losses, particularly in industries reliant on routine cognitive tasks. Reports indicate that automation in manufacturing and service sectors has intensified, leading to a “harsh filter” effect, where many workers find themselves redundant. This has raised concerns about the long-term implications for an economy that heavily relies on labor-intensive industries.
Conversely, Singapore‘s approach to AI adoption has yielded a more promising outcome. By investing in upskilling programs and fostering a culture of innovation, the nation has managed to integrate AI into its workforce without significant job losses. Government initiatives aimed at enhancing digital literacy and technical skills have empowered workers to adapt to new technologies. The result is a more resilient labor market where AI serves as a complement to human capabilities rather than a replacement.
Despite the contrasting outcomes in these two regions, the broader implications of AI on the labor market extend beyond job displacement. In Singapore, AI has been instrumental in driving economic growth, with sectors such as finance and healthcare experiencing enhanced productivity. The government’s proactive stance on AI has seen collaborations with technology firms like Microsoft and Nvidia, which have facilitated the development of AI-driven solutions tailored to local needs.
In China, however, the rapid deployment of AI technologies has sparked concerns about the quality of employment and the skills gap among the workforce. As low-skill jobs diminish, there is a pressing need for a strategic response to equip workers for the evolving job landscape. Without significant investment in education and training, many Chinese workers may struggle to transition into more skilled roles, exacerbating the country’s unemployment challenges.
The contrasting experiences of these two nations highlight the critical importance of policy frameworks in shaping AI’s impact on labor markets. In the case of Singapore, proactive engagement with stakeholders, including educational institutions and industry leaders, has created an ecosystem conducive to innovation. Meanwhile, China‘s approach appears reactive, often prioritizing rapid implementation over comprehensive workforce planning.
As the global labor landscape continues to evolve, the lessons drawn from China and Singapore may serve as guiding principles for other nations grappling with the advent of AI. Policymakers worldwide must consider strategies that not only harness the potential of AI but also safeguard employment and promote inclusivity. The future of work will likely depend on the ability of governments and industries to collaborate in creating a balanced framework that embraces technological advancements while protecting workers’ rights.
Ultimately, the ongoing discourse surrounding AI’s role in labor markets serves as a vital reminder of the need for foresight in addressing the challenges posed by technological advancements. As the integration of AI technologies deepens, nations must prioritize workforce resilience and ensure that the benefits of innovation are shared equitably. This is critical not only for economic stability but also for societal cohesion in an increasingly automated world.
For more on AI’s impact across various sectors, visit OpenAI and Microsoft.
See also Rokid Launches AI Glasses Style: Screenless, Lightweight, and $80 Cheaper than Meta’s Ray-Bans
Rokid Launches AI Glasses Style: Screenless, Lightweight, and $80 Cheaper than Meta’s Ray-Bans Vanessa Larco Forecasts 2026 Consumer AI Surge; M&A Activity and Niche Opportunities Ahead
Vanessa Larco Forecasts 2026 Consumer AI Surge; M&A Activity and Niche Opportunities Ahead Anthropic’s Daniela Amodei Reveals AI Lacks Human-Like Reasoning Despite Progress
Anthropic’s Daniela Amodei Reveals AI Lacks Human-Like Reasoning Despite Progress Gartner Cuts Revenue Growth Forecast Amid AI Concerns and Slowing Contract Value
Gartner Cuts Revenue Growth Forecast Amid AI Concerns and Slowing Contract Value