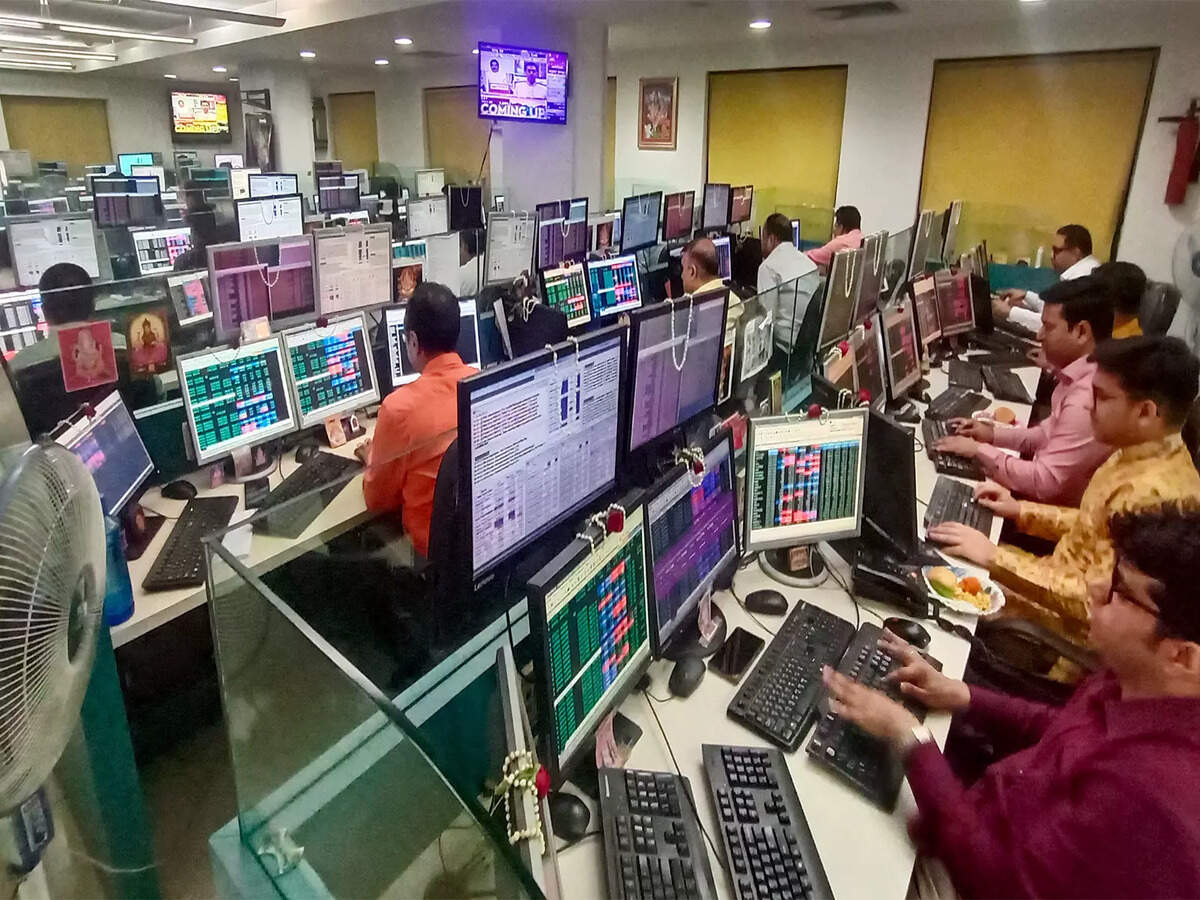
Shares of companies in the cybersecurity solutions sector experienced significant declines following the announcement by the American-based AI firm Anthropic PBC of a new tool capable of autonomously identifying and addressing software vulnerabilities. At the time of reporting, shares of JFrog had fallen by 24%, CrowdStrike Holdings by 8%, Okta by over 9%, and GitLab by over 8%.
Other companies in the field, including Zscaler, Rubrik Inc, and Palo Alto Networks, also saw sharp declines in their stock prices, illustrating a broader market reaction to the announcement.
Anthropic’s new capability, named Claude Code Security, is integrated into its Claude Code platform and is currently available in a limited research preview. The company stated that the tool is designed to “scan codebases for security vulnerabilities and suggest targeted software patches for human review,” aiming to help teams detect security issues that traditional methods often overlook.
The introduction of this tool underscores a growing trend in the cybersecurity landscape, as it seeks to empower organizations with advanced solutions to defend against emerging threats categorized as AI-enabled attacks. “We’re releasing it as a limited research preview to Enterprise and Team customers, with expedited access for maintainers of open-source repositories, so we can work together to refine its capabilities and ensure it is deployed responsibly,” added the company in its statement.
The unveiling of Claude Code Security has heightened investor concerns about the potential impact of generative AI and automated coding tools on traditional software companies. This anxiety resonates within the broader tech industry, as firms assess how these innovations may affect their business models and profit margins moving forward.
As the cybersecurity landscape evolves with the incorporation of AI technologies, market participants are closely monitoring the implications for established players in the industry. The market’s reaction to Anthropic’s announcement reflects not just immediate financial impacts but also a wider unease regarding the competitive landscape shaped by rapid technological advances.
The foray of AI into cybersecurity raises questions about the future of traditional security solutions. While tools like Claude Code Security offer promising capabilities for identifying vulnerabilities, they also signal a shift in how security measures are implemented and managed. Companies reliant on conventional methodologies might find themselves at a disadvantage if they do not adapt to this new environment.
As the development of AI-driven security tools continues, industry stakeholders remain vigilant about the evolving threat landscape. Future advancements in AI may further reshape the dynamics of cybersecurity, compelling traditional companies to innovate or reevaluate their strategies. The ongoing developments in this field are set to redefine not only security practices but also the financial health of firms involved in cybersecurity.
See also Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere
Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere 95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT
95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT AI in Food & Beverages Market to Surge from $11.08B to $263.80B by 2032
AI in Food & Beverages Market to Surge from $11.08B to $263.80B by 2032 Satya Nadella Supports OpenAI’s $100B Revenue Goal, Highlights AI Funding Needs
Satya Nadella Supports OpenAI’s $100B Revenue Goal, Highlights AI Funding Needs Wall Street Recovers from Early Loss as Nvidia Surges 1.8% Amid Market Volatility
Wall Street Recovers from Early Loss as Nvidia Surges 1.8% Amid Market Volatility