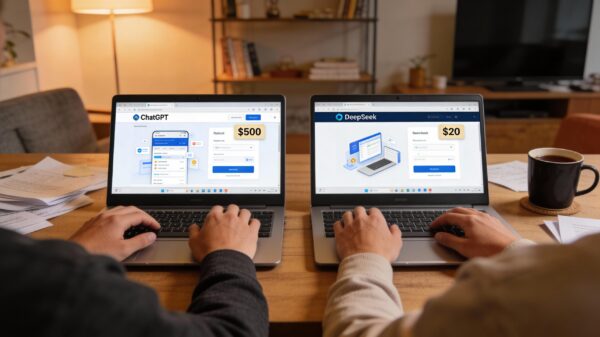
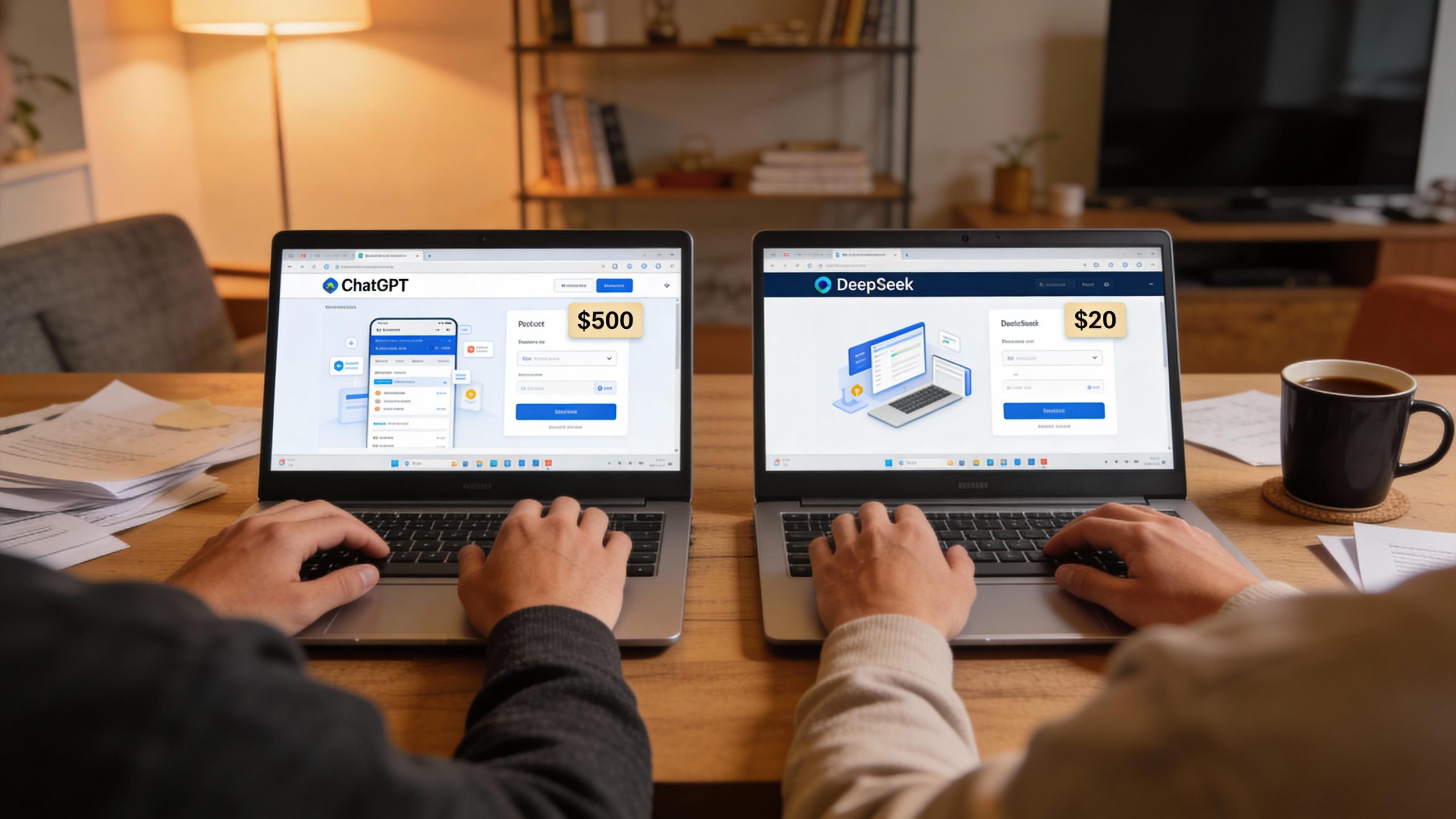
DeepSeek R1 has achieved a notable milestone, matching the performance of ChatGPT on key benchmarks while dramatically reducing costs, training for $5.5 million on 2,048 chips in contrast to OpenAI’s expenditure of over $100 million on more than 16,000 chips. For developers engaged in high-volume coding or mathematical tasks, this cost differential is significant, translating into a potential monthly API bill of $20 versus $500.
The efficiency gap may seem exaggerated until one examines the underlying architecture: the Mixture-of-Experts model activates only 37 billion parameters per query, rather than exhausting a full dense model’s 671 billion. Early adopters, particularly in STEM fields, are beginning to shift towards DeepSeek for specific applications like R/Python debugging, where its specialized Coder model achieves performance in the 96th percentile.
However, DeepSeek is not positioned as a direct replacement for ChatGPT for the average user. While it excels in logic puzzles and produces cleaner code, it struggles with tasks requiring conversational fluency, such as crafting engaging email subject lines or generating images. ChatGPT retains its dominance in natural language tasks, where creativity and multi-topic engagement are paramount, outperforming DeepSeek in areas where vivid writing is crucial.
The divide between the two platforms is clear: DeepSeek serves as a high-precision tool for developers, whereas ChatGPT functions as a versatile productivity assistant for a broader audience. Users whose work involves storytelling, brainstorming, or multimodal tasks may find DeepSeek’s limitations, including censorship issues associated with its China-hosted infrastructure, a significant barrier. Rather than having a clear consensus on superiority, both tools cater to different user needs—one for engineers and the other for the general public.
A critical aspect of evaluating DeepSeek’s appeal is the lack of real-world use cases to substantiate its advantages. To date, no developer communities have publicly detailed any significant transitions from ChatGPT to DeepSeek, citing concrete savings or performance failures. Although general cost benefits are evident, testimonials and verified transitions remain absent. OpenAI has yet to announce any price reductions or indicate a growing competitive threat, suggesting that DeepSeek’s cost-saving potential may not yet disrupt the market.
This situation creates a perception that, while DeepSeek is technically advanced, its adoption is still limited to niche applications. The efficiency of the Mixture-of-Experts model is tangible; however, the absence of widespread acceptance raises questions about whether DeepSeek can truly compete with mainstream offerings. The measures taken by developers to migrate from ChatGPT to DeepSeek remain largely undocumented, adding to the uncertainty regarding its market position.
For those considering which platform to utilize, the choice is becoming clearer. DeepSeek is ideal for running high-volume API calls focused on coding, mathematical proofs, or logic-intensive automation, where accuracy takes precedence over stylistic refinement. With cost savings of 27 times on output tokens—$2.19 compared to ChatGPT’s $60 per million—it presents an appealing option for startups that heavily rely on backend operations.
Conversely, ChatGPT is still the go-to application for creative writing, brainstorming, image generation, and workflows that benefit from plugins and multimodal capabilities. The gap in ecosystem support is evident; while DeepSeek’s open-source R1 model competes effectively with OpenAI’s offerings in certain technical tasks, it lacks integration with platforms like Slack or the ability to generate images through DALL-E. Ultimately, DeepSeek emerges as an efficiency leader for technically skilled users who understand their specific requirements, while ChatGPT continues to serve as a reliable daily driver for a wider audience. The discussion isn’t about which tool is inherently better; it’s about identifying which tool best addresses your current needs.
See also EU Leaders Convene in Dubai to Tackle AI, Trade, and Geopolitical Challenges
EU Leaders Convene in Dubai to Tackle AI, Trade, and Geopolitical Challenges Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere
Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere 95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT
95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT AI in Food & Beverages Market to Surge from $11.08B to $263.80B by 2032
AI in Food & Beverages Market to Surge from $11.08B to $263.80B by 2032 Satya Nadella Supports OpenAI’s $100B Revenue Goal, Highlights AI Funding Needs
Satya Nadella Supports OpenAI’s $100B Revenue Goal, Highlights AI Funding Needs