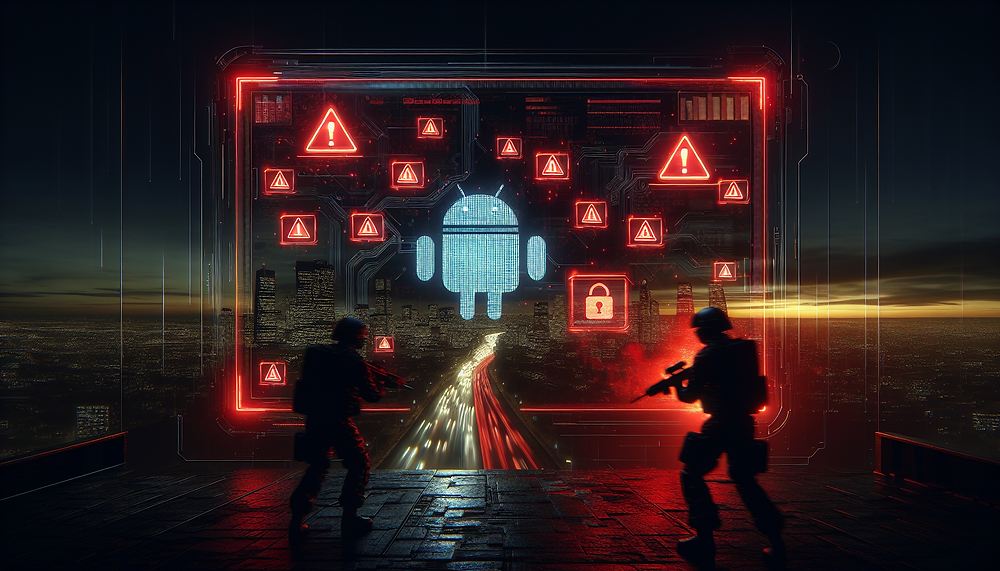
A large-scale Android malware campaign has been uncovered, exploiting the trusted platform Hugging Face to distribute thousands of polymorphic malware variants. This operation was first reported by Bitdefender and has since garnered widespread attention in the security community. The campaign primarily targets Android users by masquerading as a fake security application called TrustBastion, which operates as a sophisticated Remote Access Trojan (RAT). By leveraging Android Accessibility Services, the malware is capable of stealing credentials, monitoring user activity, and maintaining persistent control over infected devices. The campaign showcases advanced evasion tactics, such as rapid server-side polymorphism and infrastructure rebranding, raising significant concerns about the misuse of trusted AI and machine learning platforms for malicious purposes.
The threat actors behind this operation are not conclusively linked to any known Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) group. Instead, their operational traits suggest a focus on financially motivated cybercriminals. The campaign exhibits a high level of technical sophistication, including the automation of malware payload generation and the exploitation of legitimate cloud infrastructure for distribution. Following initial takedowns, the actors swiftly rebranded their malware from TrustBastion to Premium Club, demonstrating a keen awareness of the threat landscape and agility in their tactics. The use of trustbastion[.]com as a command-and-control (C2) server and the incorporation of Hugging Face datasets indicates a well-resourced group experienced in mobile malware distribution.
The attack typically begins with social engineering tactics that lure victims into downloading the malicious application, often through scareware advertisements. Once the TrustBastion APK is installed, it presents a counterfeit Google Play update dialog to coerce users into installing an additional “update” for continued protection. This initial dropper then connects to the C2 infrastructure, redirecting the device to a malicious dataset repository hosted on Hugging Face. The final payload, a polymorphic APK, is retrieved via the Hugging Face Content Delivery Network (CDN). The malware’s creators employ server-side polymorphism, generating approximately 6,000 unique payloads within a month, significantly complicating detection efforts.
The core capabilities of this malware revolve around its abuse of Android Accessibility Services. Once granted permissions, the RAT can overlay phishing screens on legitimate applications, capture user input, and prevent uninstallation attempts. Credential theft is executed through overlays mimicking popular financial applications such as Alipay and WeChat. The malware maintains persistent C2 communication, allowing for real-time data exfiltration and remote command execution. After initial takedowns, the operation quickly resurfaced under the name Premium Club, with minimal changes to its visual identity but retaining its foundational malicious code.
This malware campaign has chiefly targeted Android users in the Asia-Pacific region, focusing on extracting credentials from popular mobile payment platforms like Alipay and WeChat. The distribution of the malware occurs exclusively through sideloading, as there is no evidence of its presence on the legitimate Google Play ecosystem. Infection vectors include direct download links shared through malicious advertisements, phishing messages, and compromised websites. The malware establishes persistence by utilizing Accessibility Services, effectively preventing its uninstallation while maintaining control over the device.
The victims of this campaign are primarily individual Android users, particularly those in the Asia-Pacific region who frequently use mobile payment services. The phishing overlays displayed are tailored to closely resemble the interfaces of Alipay and WeChat, indicating a strategic approach aimed at financial credential theft. Current findings suggest no targeting of specific industries or government entities, with the distribution methods pointing toward a broad and opportunistic targeting strategy.
To combat this threat, organizations and individuals can implement a combination of technical controls and user education. Blocking access to known malicious infrastructure, like trustbastion[.]com and dubious Hugging Face dataset URLs, is crucial. Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions should be configured to prevent sideloading of APKs, reducing infection risks from unauthorized sources. User awareness is vital; educating users about the dangers of installing apps from outside the Google Play store and the risks associated with granting Accessibility Service permissions to untrusted applications can enhance defenses.
Regular updates of mobile security solutions and enabling features such as Google Play Protect can provide further protection by detecting and blocking known malware variants. Organizations should maintain up-to-date blocklists of indicators of compromise (IOCs) and vigilantly monitor network traffic for connections to suspicious domains and CDNs. The evolving nature of this malware campaign underscores the need for heightened vigilance and adaptive strategies in the ongoing battle against cyber threats.
See also Taiwan AI College Alliance Surges to 6,109 Enrollments, Boosting Course Completion Rates to 75.7%
Taiwan AI College Alliance Surges to 6,109 Enrollments, Boosting Course Completion Rates to 75.7% Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere
Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere 95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT
95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT AI in Food & Beverages Market to Surge from $11.08B to $263.80B by 2032
AI in Food & Beverages Market to Surge from $11.08B to $263.80B by 2032