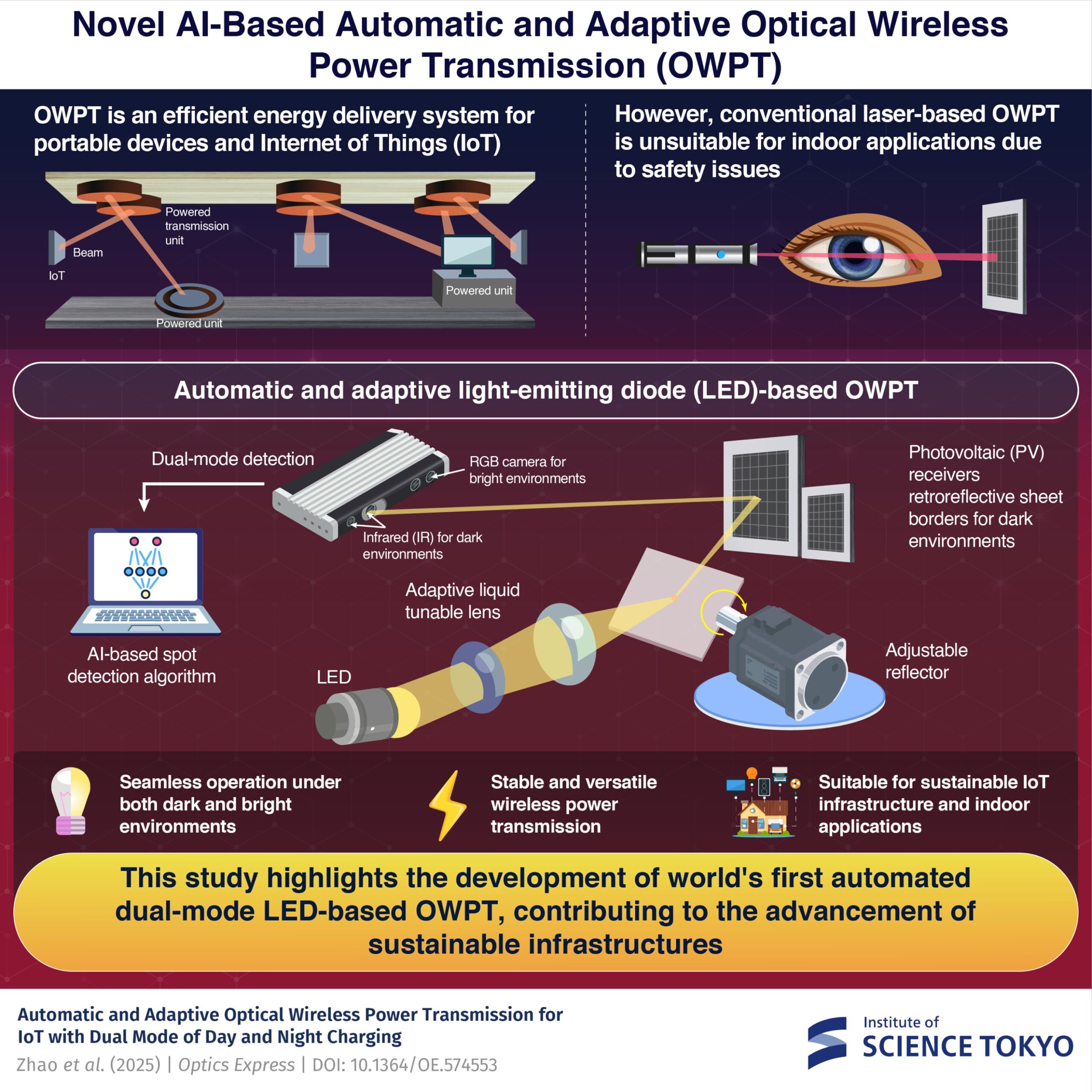
Researchers at the Institute of Science Tokyo have unveiled the world’s first automatic and adaptive dual-mode light-emitting diode (LED)-based optical wireless power transmission (OWPT) system. This innovative technology operates efficiently in both dark and brightly lit environments, enabling it to power multiple devices without interruption. As the demand for flexible power solutions grows alongside the rapid development of the Internet of Things (IoT), this low-cost and safe system presents a viable alternative to traditional power delivery methods like batteries and cables.
Traditional power solutions often face limitations: batteries require frequent recharging and replacement, while cables can restrict device mobility. In contrast, optical wireless power transmission offers a solution by converting electricity into light, transmitting it through free space, and then reconverting it back into electrical power using photovoltaic (PV) receivers. However, most existing OWPT systems have relied on laser technology, which can pose safety risks due to strict exposure regulations for indoor use.
LED-Based Innovation for Safer Power Delivery
The newly developed LED-based OWPT system addresses the safety concerns associated with laser systems, providing a robust and reliable power transmission method. According to Professor Tomoyuki Miyamoto and doctoral researcher Mingzhi Zhao from the Laboratory for Future Interdisciplinary Research of Science and Technology at Science Tokyo, their system adapts automatically to varying indoor lighting conditions, ensuring safe and efficient power delivery to multiple IoT devices. Their findings were published in the journal Optics Express on October 24, 2025.
To tackle challenges such as power loss over long distances and inconsistent performance in changing ambient light, the researchers integrated an adaptive lens system with a double-layer configuration. This system utilizes a liquid lens with a tunable focal length combined with an imaging lens to optimize power transmission by automatically adjusting the beam spot size based on the distance and size of the receiver.
Precision Targeting and Continuous Operation
To enhance targeting accuracy, the system incorporates an adjustable reflector, controlled by two series-connected stepping motors that allow independent rotation in both horizontal and vertical directions. A depth camera equipped with an RGB sensor and an infrared (IR) sensor facilitates precise alignment with the PV receivers. The RGB sensor identifies the receiver’s position, while the IR sensor determines where the light beam is irradiated, enabling the control system to adjust the reflector’s orientation accurately.
The design also includes retroreflective (RF) sheets around the edges of the PV receivers, which reflect IR light to create a clear outline for detection. This feature helps the system isolate the target PV area, minimizing interference from surrounding objects. Additionally, the researchers employed a convolutional neural network based on the Single Shot MultiBox Detector (SSD) algorithm to further enhance accuracy.
In experimental trials, the auto-OWPT system demonstrated its capacity to power multiple PV receivers of different sizes and at varying distances, achieving stable power transmission over distances of up to five meters. By allowing rapid switching between targets and continuous operation in different lighting conditions, the system demonstrates its versatility and effectiveness.
“Our auto-OWPT system offers a stable and versatile wireless power transmission solution,” states Miyamoto. “It will play a key role in building sustainable IoT infrastructure, particularly in smart factories, homes, and indoor environments where safe, wireless, dynamic, and scalable power delivery is essential.”
This advancement not only emphasizes the potential of LED-based technology for safe and efficient power delivery but also highlights the growing importance of sustainable solutions in the evolving landscape of IoT.
More information: Mingzhi Zhao et al, Automatic and adaptive optical wireless power transmission for IoT with dual mode of day and night charging, Optics Express (2025). DOI: 10.1364/oe.574553
See also AI Enhances Colorectal Cancer Surgery Outcomes, Reveals Systematic Review Insights
AI Enhances Colorectal Cancer Surgery Outcomes, Reveals Systematic Review Insights Anthropic Announces $50B Data Center Expansion to Power Next-Gen AI Models
Anthropic Announces $50B Data Center Expansion to Power Next-Gen AI Models Cohere and OpenAI Face Major Legal Setbacks in Copyright Infringement Cases
Cohere and OpenAI Face Major Legal Setbacks in Copyright Infringement Cases Google Photos AI Edits Blocked in Texas and Illinois Due to Biometric Privacy Laws
Google Photos AI Edits Blocked in Texas and Illinois Due to Biometric Privacy Laws