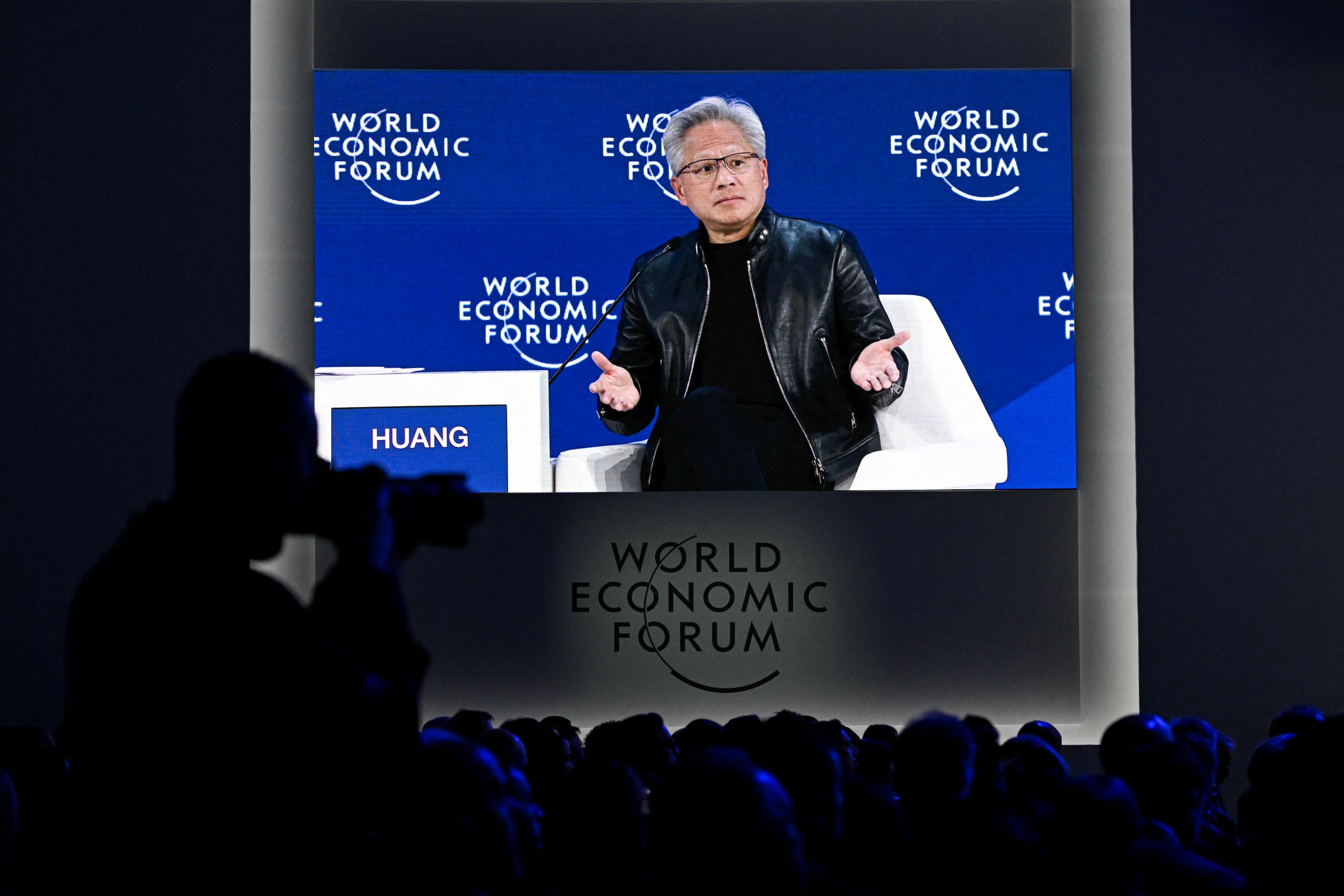
Nvidia’s H200 chips are in the spotlight following revelations that they are set to be supplied to military firms in China, raising significant concerns among U.S. officials. The involvement of these chips, designed for AI applications, highlights the growing intersection of advanced technology and military capabilities, which has intensified scrutiny regarding foreign technology transfers.
The H200, part of Nvidia’s hardware lineup aimed at enhancing artificial intelligence functionality, has attracted attention due to its advanced specifications. Designed for high-performance computing, the H200 is touted for its capacity to handle complex AI workloads with significant efficiency. However, its potential deployment within Chinese military firms poses questions about the implications for global security and competitive balance in the AI field.
This situation is exacerbated by the increasingly strained relations between the United States and China, particularly in the technology sector. U.S. policymakers have expressed concerns over the possibility that advanced technology could bolster China’s military capabilities, potentially undermining regional stability. The Biden administration has actively sought to limit Chinese access to high-end semiconductor technology, viewing it as critical to maintaining a strategic edge.
Reports indicate that the H200 chips may be repurposed for military applications, which has prompted calls for stricter regulations on technology exports. The U.S. has previously implemented measures aimed at curtailing the flow of sensitive technology to China, particularly in the semiconductor space. Experts suggest that the sale of such advanced chips could significantly enhance the operational capabilities of Chinese military entities.
In response to the revelations regarding the H200 chips, Nvidia has stated its commitment to complying with all applicable export regulations. The company reiterated its position that it does not support the use of its technology for military purposes. However, the complexities surrounding technology transfers make it increasingly challenging to monitor how products are ultimately utilized once they leave U.S. shores.
The implications of these developments extend beyond just Nvidia, with broader ramifications for the entire semiconductor industry. As nations race to advance their AI capabilities, the stakes have never been higher. Companies involved in cutting-edge technologies must navigate a labyrinth of regulatory challenges while balancing the pressures of international competition.
Looking ahead, the situation surrounding Nvidia’s H200 chips will likely prompt renewed discussions about export controls and the need for a cohesive strategy to address the risks of technology proliferation. As geopolitical tensions continue to influence technology markets, the call for greater transparency and accountability in technology supply chains is expected to grow louder.
See also Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere
Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere 95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT
95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT AI in Food & Beverages Market to Surge from $11.08B to $263.80B by 2032
AI in Food & Beverages Market to Surge from $11.08B to $263.80B by 2032 Satya Nadella Supports OpenAI’s $100B Revenue Goal, Highlights AI Funding Needs
Satya Nadella Supports OpenAI’s $100B Revenue Goal, Highlights AI Funding Needs