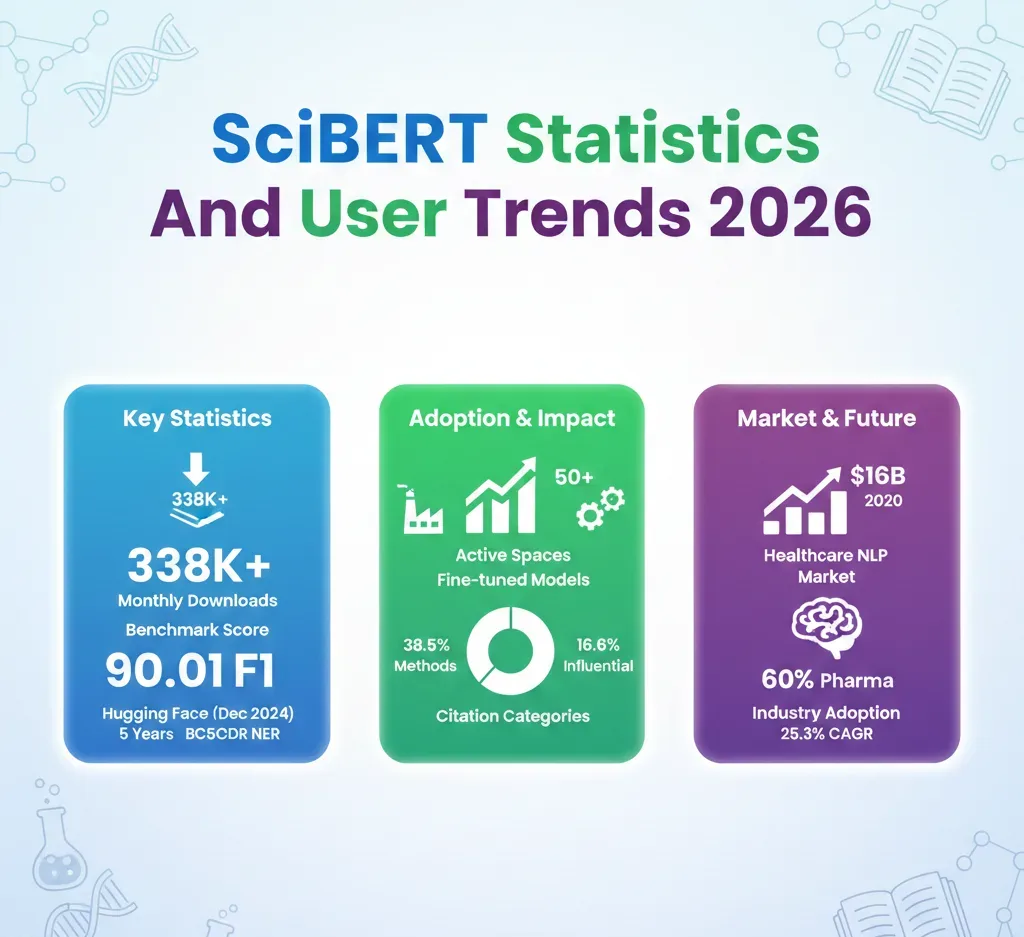
SciBERT, a model developed by the Allen Institute for AI, has solidified its status as a cornerstone in the field of scientific natural language processing (NLP) with 338,726 monthly downloads recorded on Hugging Face as of December 2024. Five years post-launch, its influence is demonstrated not only through its substantial download figures but also through its 3,394 academic citations, including 564 classified as highly influential. Furthermore, the model supports 88 fine-tuned derivative models across various research and production settings.
Demonstrating its superior performance, SciBERT achieved a remarkable 90.01 F1 score on the BC5CDR benchmark for recognizing chemicals and diseases, outpacing specialized biomedical models despite being trained on a smaller multi-domain corpus of 1.14 million scientific papers. This F1 score illustrates the model’s effectiveness in extracting relevant information, a critical task in the fast-evolving healthcare landscape.
As a primary distribution channel, Hugging Face has facilitated SciBERT’s extensive reach, with its scibert_scivocab_uncased model garnering 338,726 downloads in December alone. The repository has attracted 162 likes and enables the deployment of over 50 models within Hugging Face Spaces. Such sustained interest reflects the model’s ongoing adoption in both academic and commercial arenas.
Academic interest in SciBERT remains robust, as evidenced by citation data from Semantic Scholar. Of the total citations, 38.5% are attributed to methodological citations, indicating that researchers primarily use SciBERT as a foundational tool in their work. Background citations contribute 24.3%, while results citations are comparatively low at just 1.8% of the total. This distribution highlights SciBERT’s role as a central method in NLP research within the scientific community.
The training architecture of SciBERT is particularly noteworthy, having been developed using a dataset that includes 1.14 million full-text scientific papers from Semantic Scholar, aggregating to a staggering 3.1 billion tokens. The training corpus is predominantly biomedical, accounting for 82%, with the remaining 18% sourced from computer science literature. To enhance its efficacy, SciBERT utilizes a domain-specific vocabulary crafted with WordPiece tokenization, consisting of 31,090 tokens, which mitigates out-of-vocabulary rates for scientific terms.
Further, the model adheres to the specifications of BERT-Base, featuring 110 million parameters organized into 12 layers, with 768 hidden dimensions and 12 attention heads. The training process was conducted over seven days on TPU v3 hardware, showcasing the computational demands typical of advanced NLP models.
Benchmark results underscore SciBERT’s competitive edge in named entity recognition tasks. It achieved a score of 77.28 on the JNLPBA biomedical NER and 88.57 on the NCBI-disease dataset. However, its most substantial advantage was in relation extraction tasks, where it scored 83.64 on the ChemProt dataset, outperforming BioBERT by 6.96 points, representing a notable 9.1% improvement.
The healthcare NLP market is experiencing significant growth, valued at $5.18 billion in 2024, with projections indicating a rise to $16.01 billion by 2030. This reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.3%. Within this landscape, biomedical text mining is positioned for robust expansion, expected to grow from $1.8 billion in 2024 to $6.2 billion by 2030, translating to a CAGR of 27.4%. As organizations increasingly adopt NLP technologies, reports indicate that pharmaceutical companies have reached a 60% adoption rate for tools aimed at literary mining, and biotech firms have surpassed a 50% deployment rate for AI-driven NLP systems focused on disease pattern identification.
As the healthcare sector continues to harness the power of NLP, evidence suggests that organizations leveraging these technologies for clinical trial recruitment have achieved a 40% reduction in patient matching time, while automation of healthcare documentation has increased by 50% over a three-year measurement period. Such advancements are indicative of the transformative potential of NLP in enhancing operational efficiencies and driving innovation within healthcare.
With continued advancements in AI and NLP technologies, the role of models like SciBERT is expected to expand, influencing both research methodologies and practical applications in the healthcare domain. As adoption rates rise and the market evolves, SciBERT stands at the forefront of a new era for scientific natural language processing, paving the way for further innovations and improvements in how we understand and utilize scientific literature.
See also Mastercard: AI Adoption to Propel APAC Growth Amid Trade Disruptions and Tariff Changes
Mastercard: AI Adoption to Propel APAC Growth Amid Trade Disruptions and Tariff Changes States Defy Trump’s AI Executive Order, Continue to Enact Regulations to Protect Consumers
States Defy Trump’s AI Executive Order, Continue to Enact Regulations to Protect Consumers Nebius Group Faces Stock Decline Amid $17.4B Microsoft Deal and Capital Intensity Concerns
Nebius Group Faces Stock Decline Amid $17.4B Microsoft Deal and Capital Intensity Concerns LG’s webOS Update Mandates Copilot AI on TVs, Sparking User Outcry Over Privacy Risks
LG’s webOS Update Mandates Copilot AI on TVs, Sparking User Outcry Over Privacy Risks Lunit and Daiichi Sankyo Partner to Accelerate AI-Driven Cancer Biomarker Discovery
Lunit and Daiichi Sankyo Partner to Accelerate AI-Driven Cancer Biomarker Discovery