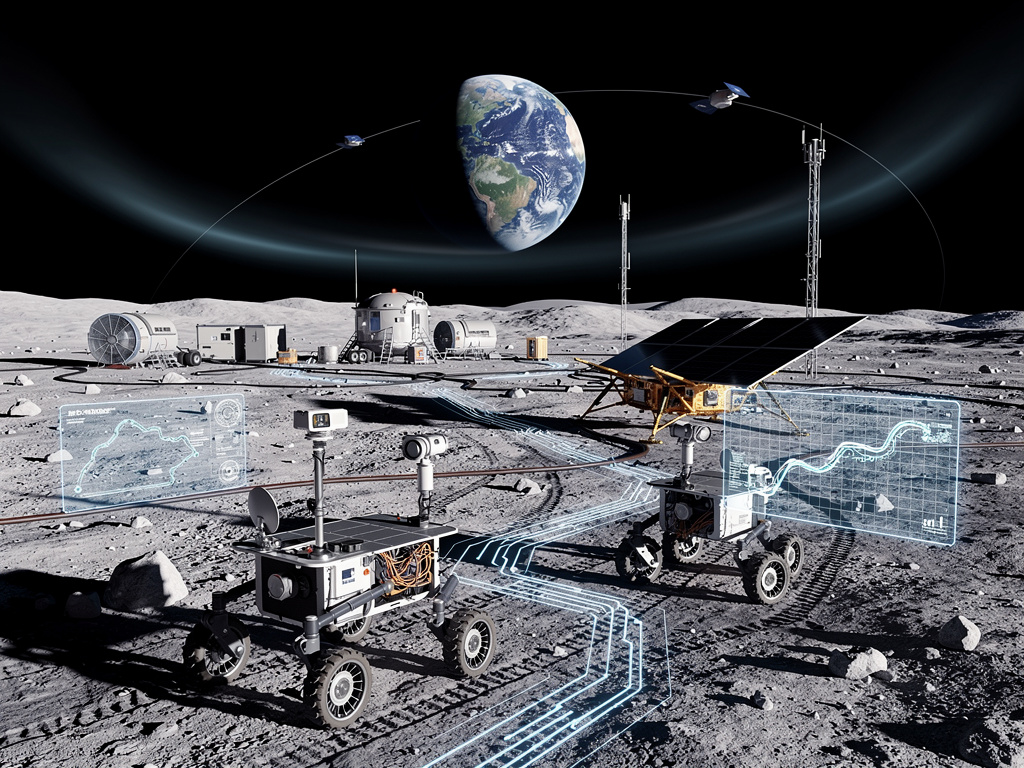
Artificial intelligence (AI) is making significant strides in space exploration, with its application now extending beyond Earth to lunar missions. As NASA advances its Artemis program, AI is being integrated into various aspects of lunar exploration, enhancing autonomous operations, data analysis, and decision-making in environments where human presence is limited. The Moon is positioned as a major testing ground for these technologies, crucial for future human settlements and scientific discoveries.
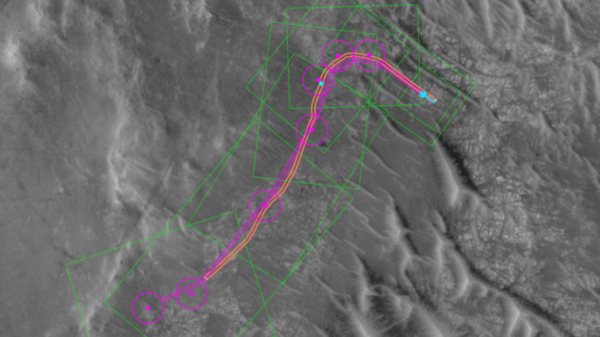
The evolution of AI in space exploration can be traced back to earlier experiments, but recent improvements in computational power have accelerated its adoption. A prime example is NASA’s Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER), which employs AI algorithms to evaluate terrain risks and optimize navigation paths. Scheduled to land near the lunar South Pole, VIPER utilizes machine learning to interpret data from historical orbiters, enabling it to navigate autonomously without reliance on Earth-based control.
AI’s role extends beyond navigation; it is transforming how data from lunar missions is processed. NASA’s systems analyze spectral data to identify water ice and other volatiles, essential for future human habitation on the Moon. This efficiency not only expedites scientific discovery but also lessens the communication bandwidth needed between the Moon and Earth, where transmission delays can be significant.
One of the most compelling applications of AI is in autonomous rovers operating under harsh lunar conditions, characterized by extreme temperatures, dust, and radiation. The VIPER mission exemplifies how AI aids in site selection and path planning by utilizing lunar landmarks captured by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. This technology compensates for the absence of GPS on the Moon, leveraging visual recognition and pattern matching instead.
Industry experts have noted the robustness of these AI systems, which incorporate redundancies to handle potential failures. For instance, AI agents can simulate various scenarios before executing maneuvers, minimizing risks in real-time operations. This meticulous approach is vital for missions where a single mistake could jeopardize years of preparation and funding.
Private sector involvement is further enhancing these efforts. Companies like Intuitive Machines are collaborating with NASA under the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative to transport AI-enhanced payloads to the Moon. A recent announcement from NASA Marshall highlighted the importance of these partnerships in advancing robotic missions that employ AI for autonomous scientific analyses.
As lunar missions evolve from exploration to resource exploitation, AI is crucial for in-situ resource utilization (ISRU), which involves harvesting local materials for fuel, oxygen, and construction. Advanced algorithms will identify optimal mining sites by analyzing geological data and predicting resource yields such as helium-3 or regolith-based building materials. An article in Nature anticipates that AI will significantly influence discoveries in lunar research by 2026.
While the potential for AI to enable fully autonomous operations is promising for long-term lunar bases, challenges remain. Ensuring AI reliability in the Moon’s harsh environment is a priority, prompting engineers to develop radiation-hardened chips and error-correcting codes. These measures are informed by previous missions, such as those involving Mars rovers, which have utilized similar technologies to extend operational lifespans.
The data generated by lunar missions is immense, necessitating the use of AI for pattern recognition and anomaly detection. NASA’s recent AI applications include mission support tasks, such as trend analysis and system development, ensuring that AI is responsibly integrated into space operations. Moreover, AI is enhancing imaging and interferometry capabilities on the Moon, with proposals for a lunar Long-Baseline Optical Imaging Interferometer set to leverage AI for high-resolution astronomical observations.
As the collaboration between government agencies and private companies strengthens, AI’s deployment on the Moon is gaining momentum. Elon Musk’s ventures are also drawing attention, with potential AI investments extending to space missions. On the global stage, India’s Aditya-L1 spacecraft, as reported in Nature, will utilize AI-enhanced data processing to observe solar activity, indirectly benefiting lunar missions through improved space weather predictions.
As AI systems land on the Moon, ethical considerations arise regarding autonomy and decision-making authority. Experts in the industry discuss the balance between machine independence and human oversight, especially in situations involving resource allocation or emergency response. NASA emphasizes responsible AI usage, ensuring systems align with mission objectives while minimizing unintended consequences.
The strategic implications of AI in lunar exploration are becoming evident, as nations and enterprises investing in these technologies position themselves favorably for future space endeavors. Recent discussions suggest that AI-driven lunar missions could redefine global research landscapes by 2026, highlighting the geopolitical stakes involved.
Looking ahead, AI’s potential applications could include swarm robotics, where multiple AI units collaborate on tasks such as habitat assembly. Inspired by concepts from NASA’s Ames research, these advancements may enhance the efficiency of lunar operations. Furthermore, integration with quantum computing could amplify AI’s capabilities, enabling real-time simulations of lunar geology and accelerating discovery processes.
The advent of AI on the Moon represents a fundamental shift in how humanity approaches space exploration. By empowering machines to think, adapt, and operate autonomously in extraterrestrial terrains, we are not simply deploying technology; we are laying the groundwork for a multi-planetary future. As we move toward 2026, with the Artemis 2 mission poised for lunar orbit, AI will be central to ensuring crew safety and mission success, unlocking new scientific frontiers and fundamentally reshaping our understanding of the cosmos.
See also AMD and Google Partner with Samsung for U.S. 2nm AI Chip Production in Texas
AMD and Google Partner with Samsung for U.S. 2nm AI Chip Production in Texas Study Reveals AI in Healthcare Reflects Human Biases, Challenging Accountability Norms
Study Reveals AI in Healthcare Reflects Human Biases, Challenging Accountability Norms AI inside Inc. Stock Falls 4.37% to JPY 2582; Future Forecasts Signal Mixed Outlook
AI inside Inc. Stock Falls 4.37% to JPY 2582; Future Forecasts Signal Mixed Outlook NVIDIA GPUs Drive AI Boom as Data Center Sales Surge, Stock Hits New Highs
NVIDIA GPUs Drive AI Boom as Data Center Sales Surge, Stock Hits New Highs