Beijing, Dec. 19, 2025 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — In a significant advancement for evaluating artificial intelligence, the Institute of Artificial Intelligence of China Telecom (TeleAI) has unveiled a pioneering metric known as Information Capacity. This new assessment tool promises to reshape how large language models (LLMs) are analyzed, moving beyond traditional size-based metrics to focus on a model’s efficiency in knowledge compression and processing relative to its computational cost.
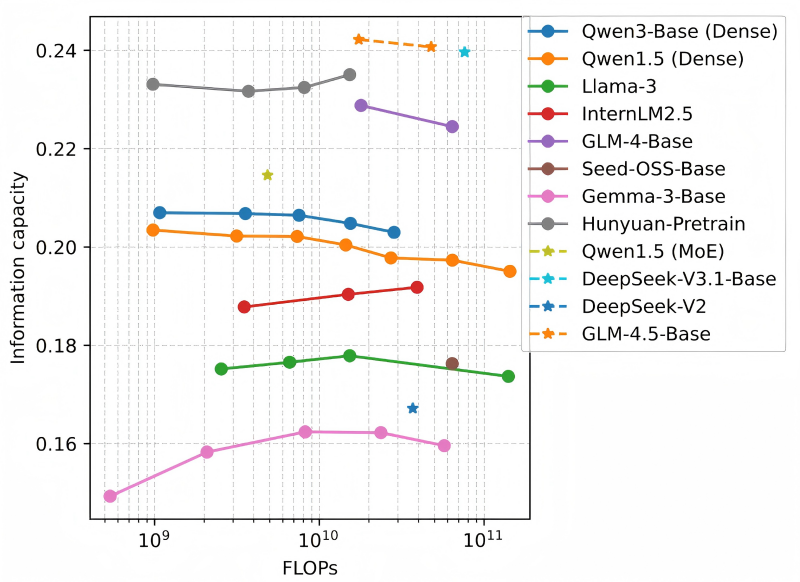
The concept of information capacity serves as a ratio between model intelligence and inference complexity, akin to a sponge’s efficiency in absorbing water. Thus, the greater the water absorbed and the faster the absorption, the more “intelligent” the model is perceived to be. Experimental results have indicated that models of differing sizes within a series display consistent information capacity. This consistency allows for a fair efficiency comparison across various model series and enables more accurate performance predictions within a single model series.
Under the leadership of Professor Xuelong Li, the CTO and Chief Scientist of China Telecom, the TeleAI research team has utilized information capacity as a metric to gauge an LLM’s talent. Their approach is driven by a strong correlation between compression and intelligence, providing a quantitative measurement of an LLM’s efficiency based on its compression performance relative to its computational complexity. This new metric reveals the intelligence density generated by a model per unit of computational cost and aids in the optimal allocation of computing and communication resources under the AI Flow framework.
As the inference workloads for large models increase, consuming more computational resources and energy, the need for accurate evaluations of inference efficiency has gained momentum among LLM researchers. With the introduction of information capacity, TeleAI has established a means to evaluate the efficiency of large models across different architectures and sizes. Additionally, this metric can effectively inform model pre-training and deployment strategies.
This research not only delivers a quantitative benchmark for the more environmentally sustainable development of large models but also facilitates the dynamic routing of models of varying sizes for efficiently handling tasks with different complexities. This adaptability is particularly relevant to the Device-Edge-Cloud infrastructure within the AI Flow framework, which is anticipated to transform the current cloud-centric computing paradigm as edge intelligence rapidly evolves.
To promote transparency and community collaboration, all relevant code and data from this research have been made available on GitHub and Hugging Face. This open-source initiative empowers the AI community to collectively enhance the standardization of large model efficiency evaluation. The links to access the codebase, dataset, and leaderboard are as follows: codebase, dataset, and leaderboard.
As the landscape of artificial intelligence continues to evolve at a rapid pace, the introduction of information capacity could redefine performance benchmarks for LLMs and influence future research directions. The implications of this advancement could extend well beyond academic circles, impacting various sectors reliant on AI technologies, particularly as efficiency and resource management become increasingly critical in the field.
See also Mistral AI Launches OCR 3, Reducing Costs to $1 per 1,000 Pages with Enhanced Accuracy
Mistral AI Launches OCR 3, Reducing Costs to $1 per 1,000 Pages with Enhanced Accuracy Ciena Stock Surges 147% in 2025, Poised for 111% Growth in 2026 Amid AI Data Center Boom
Ciena Stock Surges 147% in 2025, Poised for 111% Growth in 2026 Amid AI Data Center Boom DeepSnitch AI Surges: Potential 100x Gains as Blockchain Meets AI in 2026
DeepSnitch AI Surges: Potential 100x Gains as Blockchain Meets AI in 2026 Mistral AI Launches OCR 3, Achieving 74% Accuracy Boost Over Previous Version
Mistral AI Launches OCR 3, Achieving 74% Accuracy Boost Over Previous Version Mukesh Ambani Urges India to Lead Global AI Revolution, Combining Innovation with Empathy
Mukesh Ambani Urges India to Lead Global AI Revolution, Combining Innovation with Empathy