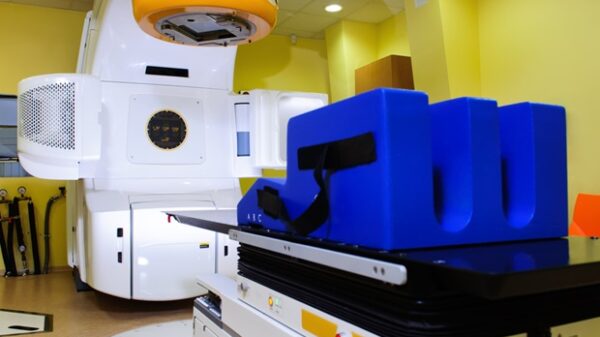
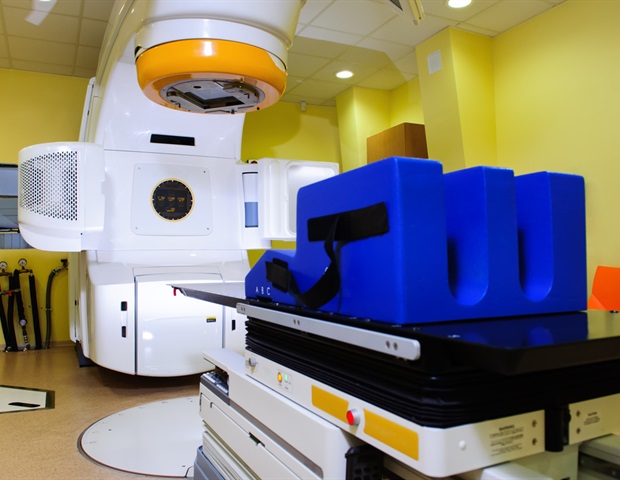
Researchers led by Professor Fu Jin have made significant strides in enhancing the efficiency of radiation therapy quality assurance (QA) by integrating advanced computational techniques. This development addresses a longstanding challenge in the field: the need to balance the computational speed and accuracy of electronic portal imaging device (EPID)-based dose verification. EPID has become instrumental for real-time in vivo dose verification, but traditional Monte Carlo (MC) simulations—considered the “gold standard” for dose calculation—face critical limitations. While increasing the number of simulated particles can improve accuracy, it dramatically extends computation times. Conversely, reducing particle counts introduces intrusive noise that can undermine the reliability of results.
To overcome these obstacles, the research team combined the GPU-accelerated MC code ARCHER with SUNet, a sophisticated deep learning architecture designed specifically for denoising. In practical applications involving lung cancer intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) cases, they generated noisy EPID transmission dose data using four different particle numbers: 1×10⁶, 1×10⁷, 1×10⁸, and 1×10⁹. The SUNet model was then trained to denoise the low-particle-number datasets, utilizing the high-fidelity 1×10⁹ particle dataset as a reference standard.
The results from this integrated MC-DL framework were promising, indicating a remarkable advancement in both computational speed and dosimetric accuracy. For instance, when denoising the originally noisy 1×10⁶ particle data, the structural similarity index (SSIM) improved from 0.61 to 0.95, while the gamma passing rate (GPR) increased from 48.47% to 89.10%. For the 1×10⁷ particle dataset, deemed optimal for balancing speed and accuracy, the denoised results achieved an SSIM of 0.96 and a GPR of 94.35%. The 1×10⁸ particle dataset reached a GPR of 99.55% after processing. Notably, the denoising step required only 0.13 to 0.16 seconds, bringing total computation times down to 1.88 seconds for the 1×10⁷ particle level and 8.76 seconds for the 1×10⁸ particle level. The denoised images exhibited significantly reduced graininess and smooth dose profiles, preserving clinically relevant features and thereby confirming the practical viability of the approach for efficient QA in radiotherapy.
This advancement has considerable implications for online adaptive radiation therapy (ART), where swift dose verification is crucial for minimizing patient discomfort and addressing anatomical changes during treatment. The method provides a versatile solution: the 1×10⁷ particle configuration achieves an optimal balance for time-sensitive scenarios, while the higher 1×10⁸ particle configuration offers increased precision for more complex cases. Professor Fu Jin emphasized the significance of this technology, stating, “By integrating the accuracy of Monte Carlo simulation with the computational efficiency of deep learning, we have developed a practical solution that addresses the critical clinical need for rapid and reliable patient-specific quality assurance.” He further noted that this innovation not only enhances existing workflows in radiation therapy but also lays the groundwork for advanced applications, such as 3D dose reconstruction, across various anatomical sites.
Looking ahead, the research team intends to expand their model to encompass additional treatment areas, further optimize the SUNet architecture, and investigate other neural network approaches to refine dose prediction capabilities. This ongoing work highlights the potential for innovative technologies in improving patient outcomes in radiation therapy.
See also AI Study Reveals Generated Faces Indistinguishable from Real Photos, Erodes Trust in Visual Media
AI Study Reveals Generated Faces Indistinguishable from Real Photos, Erodes Trust in Visual Media Gen AI Revolutionizes Market Research, Transforming $140B Industry Dynamics
Gen AI Revolutionizes Market Research, Transforming $140B Industry Dynamics Researchers Unlock Light-Based AI Operations for Significant Energy Efficiency Gains
Researchers Unlock Light-Based AI Operations for Significant Energy Efficiency Gains Tempus AI Reports $334M Earnings Surge, Unveils Lymphoma Research Partnership
Tempus AI Reports $334M Earnings Surge, Unveils Lymphoma Research Partnership Iaroslav Argunov Reveals Big Data Methodology Boosting Construction Profits by Billions
Iaroslav Argunov Reveals Big Data Methodology Boosting Construction Profits by Billions