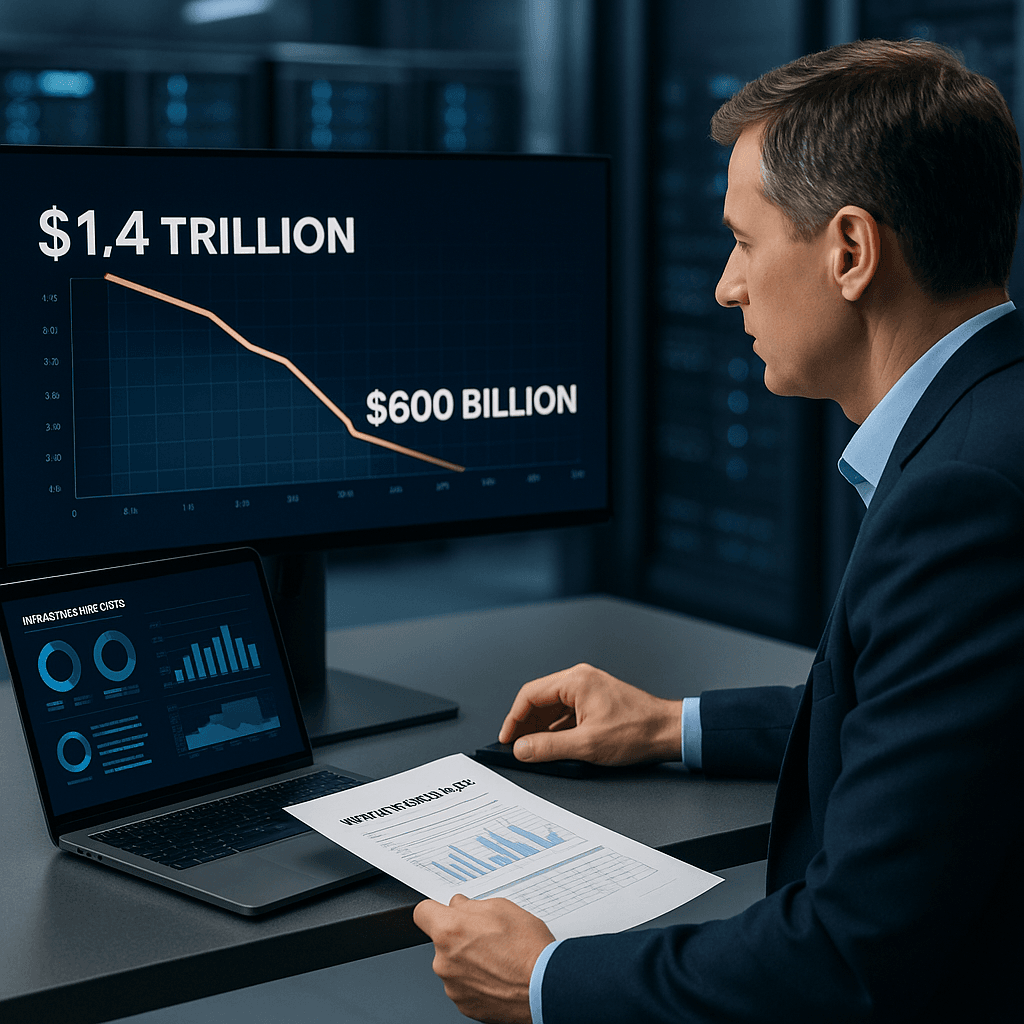
OpenAI has significantly revised its projected spending on compute infrastructure for the next seven years, cutting its forecast from $1.4 trillion to approximately $600 billion by 2030. This substantial reduction, reported by CNBC, indicates a broader reassessment within the technology sector regarding the capital requirements necessary to support the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence (AI).
The 57% decrease in OpenAI’s spending target represents one of the most notable corrections in infrastructure forecasts in tech history. This shift suggests a growing pushback from investors against what some perceive as overly ambitious financial plans, despite the ongoing AI boom. Even dominant players in AI, such as OpenAI, are now being compelled to adopt a more measured approach to their financial strategies.
The impact of this recalibration is likely to ripple throughout the AI infrastructure ecosystem. Companies that have been building data centers in anticipation of increased AI demand may now need to reassess their own expansion plans. Additionally, suppliers like Nvidia, which provides the graphics processing units (GPUs) essential for training AI models, are likely to see shifts in their order volumes as the implications of OpenAI’s revised forecast settle in.
The $800 billion reduction in spending is not a trivial matter; it exceeds the market capitalization of many Fortune 500 companies. The change reflects a growing recognition that even significant players in the AI space must demonstrate fiscal prudence alongside their technological ambitions.
What prompted this dramatic shift? Sources familiar with the situation indicate that investor scrutiny played a crucial role. While OpenAI’s flagship product, ChatGPT, has enjoyed widespread success in consumer applications, investors—including major backer Microsoft, which has invested over $13 billion—have been advocating for a more realistic approach to financial planning. The eye-catching $1.4 trillion estimate raised concerns during private funding discussions, leading some investors to question whether OpenAI’s revenue trajectory could realistically support such extensive infrastructure spending.
Following the announcement, Nvidia experienced slight volatility in after-hours trading as investors began to analyze the implications of OpenAI’s updated forecast on future GPU orders. Data center operators, who had been gearing up for expansions driven by the anticipated demand for AI capabilities, are now faced with the task of reevaluating their growth strategies in light of OpenAI’s more tempered spending expectations.
As the tech industry grapples with this recalibration, OpenAI’s decision signals a shift in how the sector views its infrastructure needs. The previous projections had contributed to an environment of inflated expectations regarding AI-related investments. Now, the focus appears to be shifting toward sustainable growth and realistic budgeting.
This revised outlook may also prompt a more cautious approach among other AI companies as they navigate their own infrastructure requirements. With significant funding still flowing into the AI sector, the recalibration of spending forecasts serves as a reminder that financial discipline is paramount for long-term success.
As the industry adjusts to this reality, attention will likely turn to how companies manage their investments and operational strategies in the years leading up to 2030. The reduced spending forecast from OpenAI may act as a bellwether for other firms, shaping the landscape of AI infrastructure investment moving forward.
See also Tesseract Launches Site Manager and PRISM Vision Badge for Job Site Clarity
Tesseract Launches Site Manager and PRISM Vision Badge for Job Site Clarity Affordable Android Smartwatches That Offer Great Value and Features
Affordable Android Smartwatches That Offer Great Value and Features Russia”s AIDOL Robot Stumbles During Debut in Moscow
Russia”s AIDOL Robot Stumbles During Debut in Moscow AI Technology Revolutionizes Meat Processing at Cargill Slaughterhouse
AI Technology Revolutionizes Meat Processing at Cargill Slaughterhouse Seagate Unveils Exos 4U100: 3.2PB AI-Ready Storage with Advanced HAMR Tech
Seagate Unveils Exos 4U100: 3.2PB AI-Ready Storage with Advanced HAMR Tech