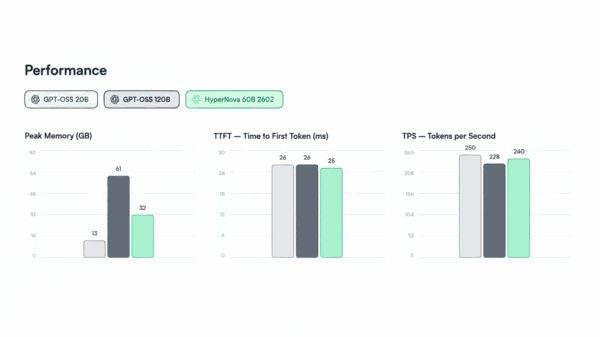
Salesforce Research’s BLIP-2, a vision-language model launched in January 2023, has amassed impressive traction with 536,142 monthly downloads on Hugging Face as of 2024. Notably, the model boasts an accuracy of 65.0% on the zero-shot Visual Question Answering v2 (VQAv2) benchmark, achieved with only 188 million trainable parameters—54 times fewer than its competitors. This blend of high performance and low parameter count has solidified BLIP-2’s significance in the evolving landscape of multimodal AI.
Since its release, BLIP-2 has garnered 3,099 academic citations by September 2024, positioning it among the top 10 most cited AI papers published in 2023. The model outperformed Flamingo80B by 8.7 percentage points on zero-shot VQAv2 tasks while utilizing significantly fewer parameters. This efficiency stems from its Q-Former architecture, which connects frozen image encoders to language models of up to 11 billion parameters, setting a new standard for efficiency in the field.
The Q-Former component is defined by its 188 million trainable parameters distributed across 12 transformer layers, producing query embeddings of 32 × 768 dimensions. This approach allows BLIP-2 to seamlessly integrate with larger language models without the need for extensive retraining. Its memory requirements can drop to just 1.8 GB with Int4 quantization, making it deployable on standard consumer hardware for inference tasks, a notable development in an era where computational efficiency is paramount.
BLIP-2’s benchmark performance further underscores its capabilities, achieving state-of-the-art results across several key tests. In addition to the aforementioned VQAv2 score, it registered 52.3% accuracy on the GQA benchmark and a CIDEr score of 121.6 on NoCaps captioning tasks, surpassing prior records. Moreover, fine-tuned versions of BLIP-2 hit 145.8 CIDEr on COCO Caption benchmarks and achieved a remarkable 92.9% accuracy on the Flickr30K image-to-text retrieval task.
The model’s zero-shot performance is particularly noteworthy, illustrating its strong generalization capabilities. Despite using dramatically fewer parameters than competing models, BLIP-2’s advancements have established a new efficiency-performance benchmark in vision-language models.
As BLIP-2 continues to gain traction within the AI community, Hugging Face reports that its blip2-opt-2.7b checkpoint maintains a steady flow of monthly downloads, now exceeding 536,000. The Salesforce organization has also cultivated a following of 1,990 on the platform. With five official model variants available, BLIP-2 supports multiple language model backends and diverse applications. Community contributions include 38 adapter models and 13 fine-tuned derivatives, reflecting a vibrant ecosystem around the framework.
BLIP-2’s academic impact is underscored by its rapid citation growth, having appeared at ICML 2023 shortly after its release. This swift integration into Hugging Face within just ten days facilitated access for researchers and developers, accelerating experimentation and application across various domains.
From a technical perspective, BLIP-2 operates efficiently across multiple precision modes. Float32 precision necessitates 14.43 GB for inference and 57.72 GB for training, while Float16 and BFloat16 reduce these requirements to 7.21 GB and 28.86 GB, respectively. Int8 quantization brings inference memory usage down to 3.61 GB, and the Int4 configuration enables deployment with a mere 1.8 GB, facilitating access on consumer-grade GPUs and edge devices.
The model’s pre-training phase leveraged 129 million image-text pairs from various datasets, employing a multi-objective learning strategy. This approach aligns image and text representations while conditioning text generation on visual features, contributing to BLIP-2’s strong performance across downstream tasks.
Comparative analyses place BLIP-2 in an interesting position against other models. While LLaVA-1.5-13B achieved an 80.0% zero-shot accuracy, BLIP-2’s 65.0% remains competitive, particularly in tasks such as captioning and image-text retrieval where extensive fine-tuning is not a prerequisite. BLIP-2’s architecture has influenced subsequent models, including derivatives like InstructBLIP, which further enhance task-specific performance through instruction tuning.
As the AI landscape evolves, the derivative models spawned from BLIP-2, including applications in image generation and video understanding, highlight its adaptability and relevance. The model not only represents a leap forward in vision-language integration but also signifies the ongoing momentum in multimodal AI research, paving the way for future innovations that leverage this foundation.
See also Artlist Launches Complete AI Video Ecosystem Revolutionizing Production in 2026
Artlist Launches Complete AI Video Ecosystem Revolutionizing Production in 2026 Healwell AI Reports 354% Revenue Surge Amid Strategic AI Focus Shift; Stock Rally Continues
Healwell AI Reports 354% Revenue Surge Amid Strategic AI Focus Shift; Stock Rally Continues Chinese AI Models Surge as Pinterest and Airbnb Choose Cost-Effective Alternatives
Chinese AI Models Surge as Pinterest and Airbnb Choose Cost-Effective Alternatives Revolutionary Riff-Diff Method Designs Custom Enzymes with Unmatched Efficiency and Stability
Revolutionary Riff-Diff Method Designs Custom Enzymes with Unmatched Efficiency and Stability AI Transforms Mobility Operations: Proven Strategies from EY and Novartis to Drive Efficiency
AI Transforms Mobility Operations: Proven Strategies from EY and Novartis to Drive Efficiency