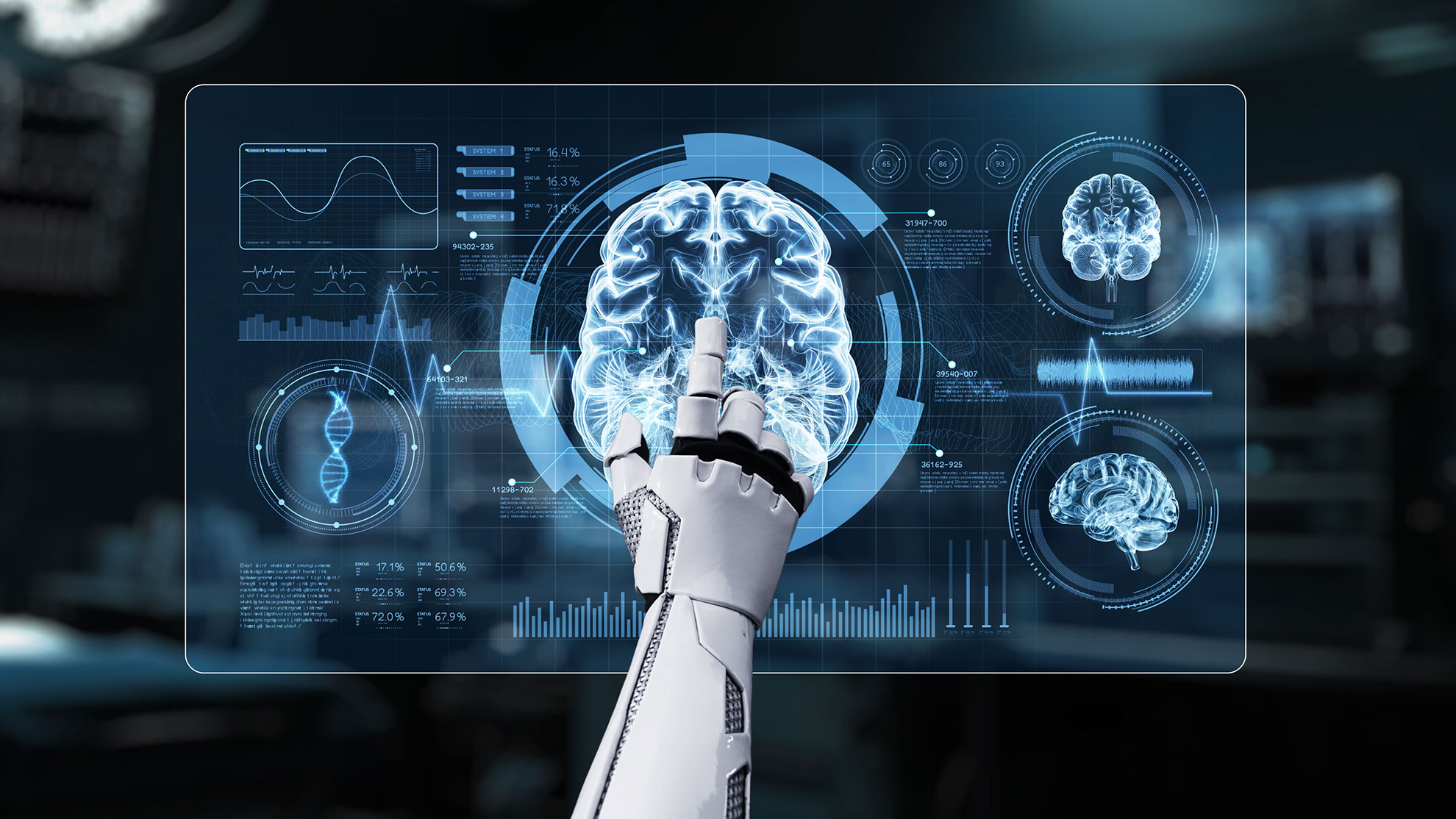
A new artificial intelligence (AI) foundation model, named BrainIAC, has been developed by researchers from Mass General Brigham, affiliated with Harvard University, demonstrating its ability to extract multiple disease risk signals from routine brain MRI scans. The model can estimate a person’s “brain age,” predict dementia risk, detect brain tumor mutations, and forecast survival rates for brain cancer patients. The findings were published in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
Trained on nearly 49,000 brain MRI scans, BrainIAC outperformed existing, more narrowly focused AI models, particularly in scenarios where training data is limited. This advantage is crucial given the challenges of acquiring large, annotated datasets, which are often necessary for conventional AI frameworks that perform specific tasks.
Brain MRI images can differ significantly based on their source and intended use—whether for neurology or oncology—which complicates the learning process for AI systems. Researchers addressed these issues by employing a technique called self-supervised learning to identify inherent features within unlabeled datasets. This method allows the model to adapt its findings for various clinical applications.
After pretraining on multiple brain MRI datasets, BrainIAC was validated against 48,965 diverse scans across seven clinical tasks of varying complexity. The model successfully generalized its learning across both healthy and abnormal MRI images, excelling in both straightforward classification tasks and more complex challenges, including the detection of specific brain tumor mutations. It consistently outperformed three traditional, task-specific AI models in these applications.
Notably, BrainIAC demonstrated a remarkable ability to predict outcomes effectively in scenarios where training data was scarce or task complexity was elevated. This adaptability suggests that the model could be valuable in real-world clinical settings, where access to well-annotated medical datasets is often limited.
“BrainIAC has the potential to accelerate biomarker discovery, enhance diagnostic tools, and speed the adoption of AI in clinical practice,” stated Benjamin Kann, corresponding author and associate professor of radiation oncology at Harvard Medical School. He emphasized that integrating BrainIAC into imaging protocols could enable clinicians to better personalize patient care and improve overall treatment outcomes.
The study was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute, as well as the Botha-Chan Low Grade Glioma Consortium. As the research continues, further testing of the BrainIAC model on a broader range of brain imaging methods and larger datasets will be essential to validate its efficacy and extend its applicability in clinical environments.
The advancements made by BrainIAC not only hold promise for enhancing the accuracy of brain disease diagnostics but also represent a significant step forward in harnessing AI’s potential to transform medical imaging and patient management.
See also Google DeepMind Launches Uncertainty-Focused AI Benchmarks for Decision-Making
Google DeepMind Launches Uncertainty-Focused AI Benchmarks for Decision-Making AI Supply Chain Fragmentation Sparks Global Sovereignty Race Among Tech Giants
AI Supply Chain Fragmentation Sparks Global Sovereignty Race Among Tech Giants Canada Urged to Invest $9B in AI Startups, Designate Champions to Compete Globally
Canada Urged to Invest $9B in AI Startups, Designate Champions to Compete Globally Mistral AI Launches Voxtral Transcribe 2 with 200ms Latency for Real-Time Transcription
Mistral AI Launches Voxtral Transcribe 2 with 200ms Latency for Real-Time Transcription Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere
Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere