Power Efficiency Enhancements for Nvidia’s DGX Spark
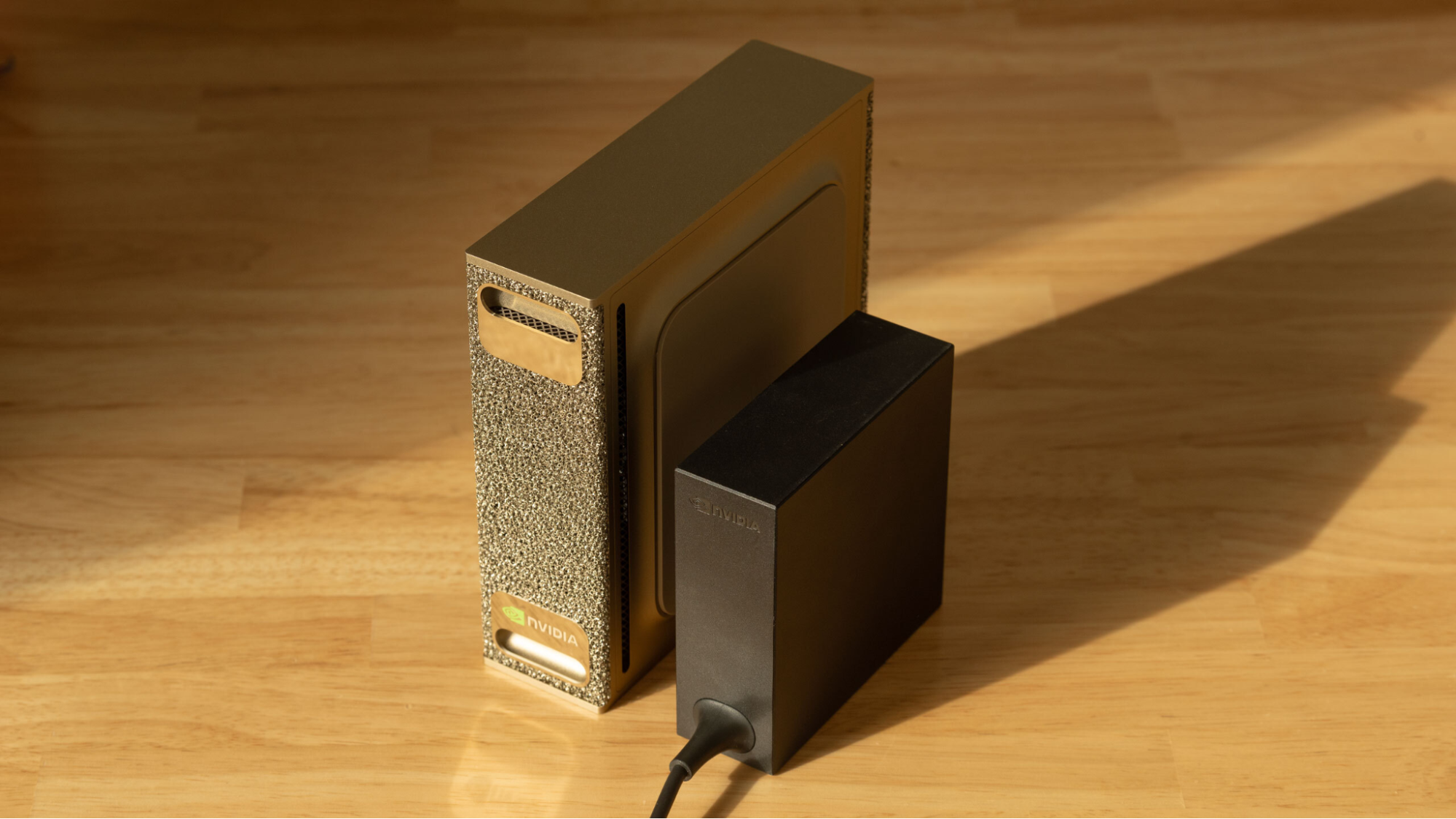
Nvidia‘s DGX Spark has emerged as a powerful local AI engine, boasting impressive specifications including 128GB of RAM, a fast 20-core Arm CPU, and the capable Blackwell GPU. In testing, the device demonstrated its versatility in handling both large language model (LLM) inference and generative workflows for images and videos. However, an unexpected finding during our review was the system’s idle power consumption, which registered around 37W. Although not alarming, this figure raised questions, particularly given the product’s advanced 3nm-class fabrication technology and Nvidia’s expertise in power management.
Recent software updates from Nvidia have unveiled the reason behind this elevated idle power draw. The introduction of hot-plug detection for the Spark’s 200Gbps ConnectX 7 NIC—an advanced networking interface—has been a significant development. Prior to this update, the NIC’s controller contributed substantially to the power usage at idle. Nvidia asserts that this enhancement can cut the system’s power consumption by up to 18W when the ConnectX 7 interface is inactive.
To verify these claims, we utilized a USB-C power meter to assess idle power consumption on the Founders Edition DGX Spark both before and after installing the latest software. The results were promising: prior to the update, the system idled at approximately 37W, whereas after the update, idle power consumption dropped to 25W with a connected display, reflecting a reduction of 32.4%. Disconnecting the display, simulating a headless server environment, revealed even further improvements, with idle power falling to just 22W.
It’s noteworthy that not every model within the GB10 series has benefited equally from this software update. Tests conducted on the Dell Pro Max GB10 system showed idle power consumption remained unchanged at 35-37W. Ongoing evaluations may yield additional insights into achieving similar reductions for this particular system.
Nvidia has also taken the opportunity to highlight various applications of the DGX Spark in educational settings. According to the company’s recent blog post, these systems are enhancing AI capabilities at institutions such as the IceCube Neutrino Observatory in Antarctica, processing radiology reports at New York University (NYU), and contributing to genetic studies on epilepsy at Harvard University.
Benedikt Riedel, computing director at the Wisconsin IceCube Particle Astrophysics Center, emphasized the significance of the Spark’s low power requirements in the extreme conditions of the South Pole. The ability to perform local analysis of neutrino observation data with a power budget of approximately 140W is invaluable in a location where both network bandwidth and power supply are critically limited. The latest update also promises to further reduce power consumption, a welcome improvement in such environments.
For current users of the DGX Spark, it is advisable to access the DGX Dashboard and navigate to the Settings tab to implement the latest software update, thus ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
See also Fashion Industry Leverages AI to Slash Costs and Boost Productivity by 2026
Fashion Industry Leverages AI to Slash Costs and Boost Productivity by 2026 SAP and Cohere Launch Sovereign AI Solutions in Canada for Secure Data Management
SAP and Cohere Launch Sovereign AI Solutions in Canada for Secure Data Management Hollywood Stars Unite Against AI: Johansson, Blanchett, Cage, Jackson, Lyonne Fight for Creative Rights
Hollywood Stars Unite Against AI: Johansson, Blanchett, Cage, Jackson, Lyonne Fight for Creative Rights AI Revolutionizes Real Estate Consulting: Bob Staedler’s Data-Driven Approach Redefines Strategy
AI Revolutionizes Real Estate Consulting: Bob Staedler’s Data-Driven Approach Redefines Strategy Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere
Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere