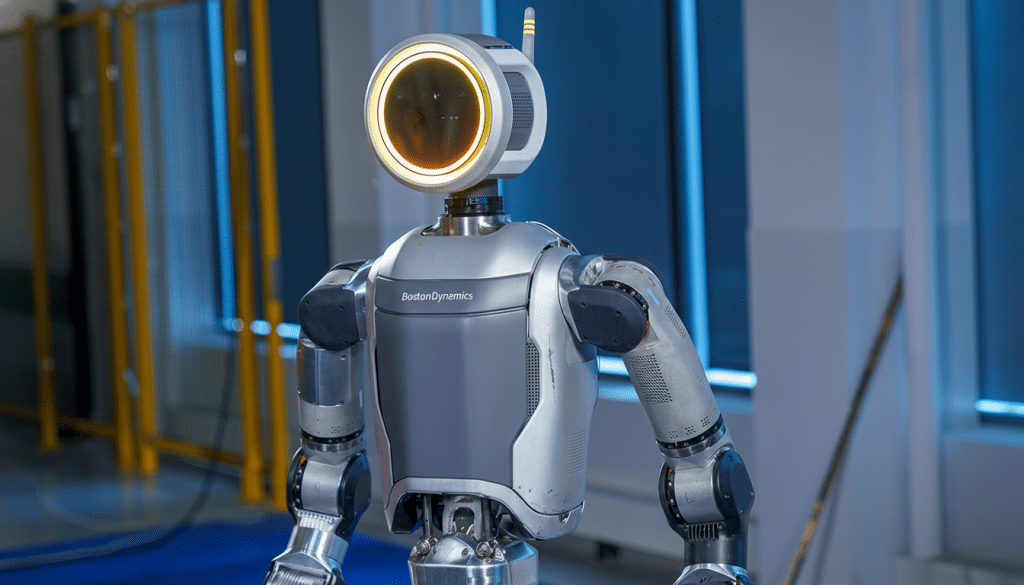
Boston Dynamics is enhancing its next-generation Atlas robot by integrating technology from Google DeepMind, aiming to create a humanoid capable of functioning in home environments. This partnership, announced with Hyundai Motor Group, seeks to equip Atlas with advanced cognitive abilities that allow it to interpret commands and perform tasks in a more humanlike manner. The collaboration is framed as a leap from laboratory testing to real-world applications, with the latest Atlas model moving toward production and set to operate on Hyundai assembly lines.
Executives from both companies described this initiative as a shortcut to practical utility, with Atlas transitioning from a research novelty to a viable solution for industrial applications. The integration of DeepMind’s artificial intelligence capabilities is expected to transform how Atlas interacts with its environment, enabling it to understand plain-language instructions, assess contextual information, and execute multi-step tasks without extensive programming.
The significance of embedding a foundation model into a humanoid robot cannot be overstated. Such integration allows Atlas to adapt to various manufacturing settings, where variability is common. By employing DeepMind’s robotics expertise, which includes advanced models for vision, language, and action, Atlas can decipher specifications and manipulate tools according to part geometries, reducing the need for costly reprogramming typically required in robotic implementations. This positions Atlas to undertake “zero-shot” behaviors, performing tasks based solely on verbal instructions, such as “grab the blue alternator from bin C and torque bolts to spec.”
Boston Dynamics is well-regarded for its pioneering advancements in robotics, particularly in locomotion and manipulation. The company’s expertise in dynamic balance and high-force actuation provides the hardware capability necessary to realize DeepMind’s intelligent policies, thus making Atlas suitable for tasks beyond simple demonstrations.
Industrial Applications and Market Landscape
The immediate focus for Atlas lies within industrial environments. With Hyundai’s extensive production ecosystem, potential applications include material handling, machine tending, and assisting with repetitive tasks that require physical labor. The versatility of humanoids allows them to navigate spaces designed for humans, such as climbing stairs or opening doors, thereby reaching areas that traditional automation cannot access.
Boston Dynamics has a track record of delivering and supporting robots on a large scale. Its quadruped robot, Spot, is currently deployed in over 40 countries, and the recently launched Stretch robot has successfully unloaded more than 20 million boxes globally. This established infrastructure—comprising service teams, spare parts, and reliability engineering—will be crucial as Atlas transitions from pilot programs to full-scale production.
Looking ahead, the integration with DeepMind is expected to emphasize device-side perception and language understanding, alongside a cloud-based model for continuous learning and updates. However, challenges such as latency, reliability, and auditability remain critical, as operators require predictable cycle times and clear documentation of the robot’s actions.
The landscape for humanoid robots is rapidly evolving, with competitors like Agility Robotics and Tesla also advancing their models for logistics and manufacturing. Analysts speculate that the market for humanoids could reach tens of billions of dollars by the mid-2030s, contingent on their reliability and cost-effectiveness. McKinsey predicts that AI-driven automation could unleash trillions in productivity annually, addressing labor market concerns regarding high turnover and strain in manual jobs.
However, the challenges of safety and human interaction present significant hurdles. As Atlas operates in proximity to people, it must not only excel in physical performance but also exhibit social awareness, understanding personal space and human intent. Compliance with safety standards such as ISO 10218 and ISO/TS 15066 will be essential, along with features like geofencing and torque-limited joints.
On the AI front, incorporating reinforcement learning and human feedback will help establish trustworthy operations. Operators will need transparent controls, such as tap-to-teach and voice commands, to ensure reliability in interactions. Additionally, the longevity of battery life and the robot’s ability to function without constant oversight will be vital to its success.
As Atlas moves closer to production, significant milestones will reveal how effectively the technology can be operationalized. Key indicators will include successful factory pilots with measurable performance metrics, the ability to generalize to new tasks rapidly, and demonstrations that DeepMind’s models can be safely updated across fleets. If Boston Dynamics and Google DeepMind can successfully merge dependable hardware with adaptive intelligence, Atlas may emerge as a pioneering humanoid, facilitating a new era of collaborative work environments.
See also J.P. Morgan Launches Special Advisory Unit to Navigate AI, Cybersecurity, and Geopolitical Risks
J.P. Morgan Launches Special Advisory Unit to Navigate AI, Cybersecurity, and Geopolitical Risks Elon Musk’s Grok AI Bot Faces Global Outcry for Generating Non-Consensual Sexualized Images
Elon Musk’s Grok AI Bot Faces Global Outcry for Generating Non-Consensual Sexualized Images NVIDIA Acquires Groq for $20B, Secures Key AI Talent and Technology Amid Market Shift
NVIDIA Acquires Groq for $20B, Secures Key AI Talent and Technology Amid Market Shift NVIDIA Unveils BlueField-4 AI Storage, Boosting Inference Efficiency by 5x for 2026
NVIDIA Unveils BlueField-4 AI Storage, Boosting Inference Efficiency by 5x for 2026 Boston Dynamics Unveils Production-Ready Atlas Robot at CES 2026: 56 Degrees of Freedom, 110-Pound Lift Capacity
Boston Dynamics Unveils Production-Ready Atlas Robot at CES 2026: 56 Degrees of Freedom, 110-Pound Lift Capacity