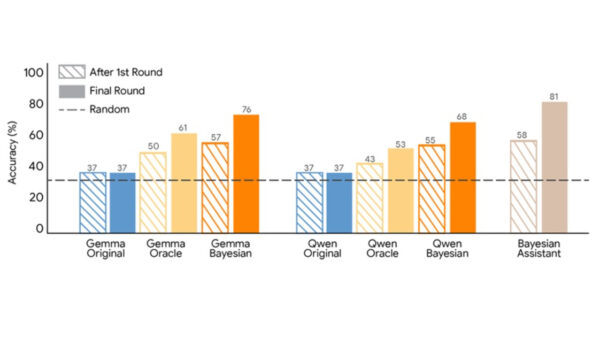
Researchers at Google DeepMind have introduced their latest artificial intelligence tool, **AlphaGenome**, which aims to assist scientists in identifying the genetic drivers of various diseases and potentially lead to new treatment options. This development was announced during a recent press briefing and is expected to enhance understanding of how genetic mutations can regulate gene activity, affecting when genes are activated, in which cells they function, and their overall biological impact.
Many common hereditary diseases, including **heart disease**, autoimmune disorders, and mental health issues, are linked to mutations that disrupt gene regulation. This also applies to various cancers, although pinpointing the specific genetic alterations responsible for these conditions remains a complex challenge. Natasha Latysheva, a researcher at DeepMind, expressed optimism about AlphaGenome, stating, “We see AlphaGenome as a tool for understanding what the functional elements in the genome do, which we hope will accelerate our fundamental understanding of the code of life.”
The human genome consists of approximately **3 billion** base pairs, with about **2%** encoding instructions for protein production, the fundamental components of life. The remaining **98%** is essential for regulating gene activity, determining when, where, and how much each gene is expressed. The researchers trained AlphaGenome using public databases of human and mouse genetics, allowing the AI to learn how mutations in specific tissues influence gene regulation. It can evaluate up to **1 million** letters of DNA code simultaneously and predict the ramifications of mutations on various biological processes.
The DeepMind team anticipates that this tool will enable scientists to identify critical strands of genetic code necessary for developing specific tissues, like nerve and liver cells, and highlight significant mutations that drive cancer and other diseases. Additionally, AlphaGenome could facilitate the creation of novel gene therapies, offering researchers the ability to design new DNA sequences tailored to activate specific genes in targeted cell types without affecting others.
Carl de Boer, a researcher at the University of British Columbia who was not involved in the study, noted, “AlphaGenome can identify whether mutations affect genome regulation, which genes are impacted and how, and in what cell types. A drug could then be developed to counteract this effect.” He emphasized that while AlphaGenome represents a considerable innovation, achieving the goal of highly accurate predictive models will necessitate continuous efforts from the scientific community.
Some scientists have already begun integrating AlphaGenome into their research. Marc Mansour, a clinical professor of pediatric haemato-oncology at University College London, described the tool as a “step change” in his pursuit of understanding the genetic drivers of cancer. Echoing this sentiment, Gareth Hawkes, a statistical geneticist at the University of Exeter, remarked on the significance of AlphaGenome, highlighting that “the non-coding genome is **98%** of our **3 billion** base pair genome. We understand the **2%** fairly well, but the fact that we’ve got AlphaGenome that can make predictions about what this other **2.94 billion** base pair region is doing is a big step forward for us.”
As AlphaGenome sets a new standard in genetic research, its potential applications in disease treatment and gene therapy underscore the transformative impact of AI on the biological sciences. With ongoing advancements, this technology may empower researchers to unravel the complexities of genetic regulation and enhance therapeutic strategies for a range of diseases, marking a significant milestone in the intersection of technology and medicine.
See also Zscaler Launches AI Security Suite, Exposing Critical Risks in Enterprise AI Systems
Zscaler Launches AI Security Suite, Exposing Critical Risks in Enterprise AI Systems Wall Street Backs Surge in Chip Equipment Spending Amid AI Boom: Key Firms to Watch
Wall Street Backs Surge in Chip Equipment Spending Amid AI Boom: Key Firms to Watch Illinois AG Leads Coalition of 35 States Urging xAI to Curb Nonconsensual AI Image Generation
Illinois AG Leads Coalition of 35 States Urging xAI to Curb Nonconsensual AI Image Generation U.S. Megacap Earnings Surge 21.5% as AI Investments Face Critical Test This Week
U.S. Megacap Earnings Surge 21.5% as AI Investments Face Critical Test This Week