MIT Researchers Harness AI to Combat Antibiotic Resistance
In an effort to address pressing global health challenges, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) are increasingly turning to artificial intelligence (AI) and quantitative modeling to develop engineered cells with unique therapeutic properties. This innovative approach aims to create new treatments for diseases, particularly in the context of antibiotic resistance, a growing concern worldwide.
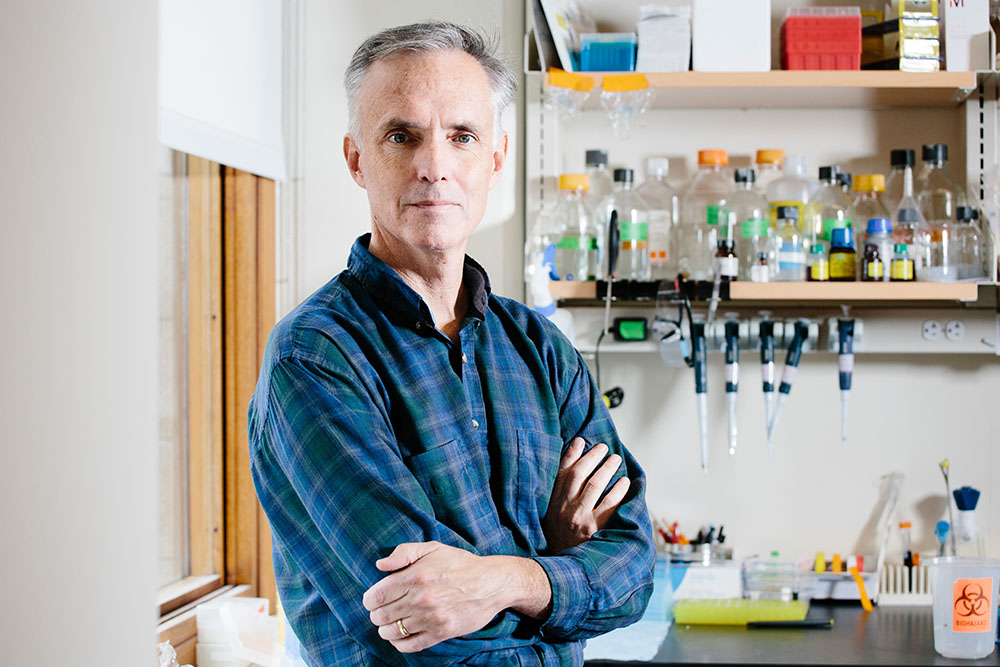
Leading the charge is James J. Collins, a pioneer in the field of synthetic biology and a prominent researcher in systems biology. Collins holds several notable positions at MIT, including Termeer Professor of Medical Engineering and Science, and he serves as the director of the MIT Abdul Latif Jameel Clinic for Machine Learning in Health. His work has propelled advancements in diagnostics and treatment options for various pathogens such as Ebola, Zika, and SARS-CoV-2, as well as antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
In a recent discussion, Collins addressed the significance of interdisciplinary collaboration in advancing his research. He emphasized that teamwork has been vital to the success of his lab’s initiatives. The collaboration with colleagues like Regina Barzilay and Tommi Jaakkola has allowed researchers to leverage deep learning to discover new antibiotics. This partnership culminated in the identification of halicin, a powerful antibiotic effective against a range of multidrug-resistant bacteria, which was published in the journal Cell in 2020.
Collins further highlighted a partnership with Donald Ingber at the Wyss Institute, utilizing organs-on-chips technology to evaluate AI-discovered antibiotics. This experimental platform simulates human tissue environments, providing a more accurate assessment of drug efficacy compared to traditional animal models, thus enhancing the understanding of therapeutic potential.
Reflecting on the advancements made in antibiotic design, Collins noted a significant breakthrough his lab achieved in 2025. The research demonstrated the potential for generative AI to create entirely new antibiotics. By employing techniques such as genetic algorithms and variational autoencoders, the team generated millions of candidate molecules. Following extensive filtering and review, they synthesized 24 compounds, seven of which exhibited antibacterial properties. Among these, one candidate, NG1, effectively targeted multidrug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae, while another, DN1, was aimed at methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Collins is optimistic about the future, mentioning that ongoing efforts involve using deep learning to enhance the drug-like properties of antibiotics. By integrating AI with high-throughput biological testing, the goal is to streamline the discovery process for safe and effective antibiotics that can be deployed in clinical settings. This proactive approach could significantly alter strategies for combating drug-resistant bacterial infections.
In addition to his research, Collins co-founded Phare Bio, a nonprofit organization dedicated to identifying new antibiotics through AI. The collaborative effort between his lab and Phare Bio aims to bridge the gap between antibiotic discovery and development. Recently, the organization received a grant from ARPA-H to develop 15 new antibiotics derived from generative AI, further extending the reach of their innovative research.
Collins stressed the importance of partnerships in this endeavor, highlighting the collaboration among biotech companies, pharmaceutical firms, and philanthropic organizations. The aim is to create a robust pipeline for the rapid development of antibiotics, aligning closely with the research objectives of MIT’s Antibiotics-AI Project.
As global health systems grapple with the escalating crisis of antibiotic resistance, Collins’s work, supported by AI advancements, represents a pivotal shift towards more proactive solutions. The integration of computational design with practical applications could provide the next generation of antibiotics, ultimately delivering critical therapies to patients facing the threat of resistant infections.
For further information about Collins’s research and the initiatives at MIT, visit the official MIT website.
See also Oklahoma Prisons Implement AI to Enhance Safety, Reduce Costs, and Streamline Inmate Releases
Oklahoma Prisons Implement AI to Enhance Safety, Reduce Costs, and Streamline Inmate Releases Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere
Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere 95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT
95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT AI in Food & Beverages Market to Surge from $11.08B to $263.80B by 2032
AI in Food & Beverages Market to Surge from $11.08B to $263.80B by 2032 Satya Nadella Supports OpenAI’s $100B Revenue Goal, Highlights AI Funding Needs
Satya Nadella Supports OpenAI’s $100B Revenue Goal, Highlights AI Funding Needs