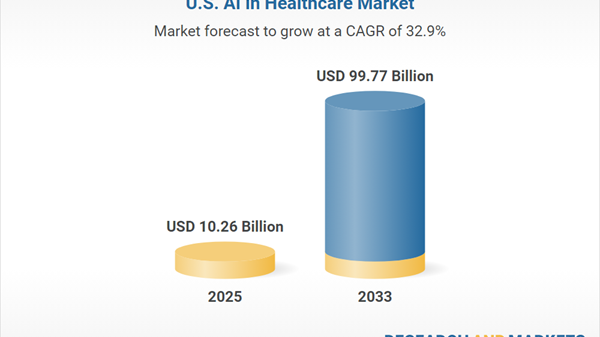
As the transformative potential of artificial intelligence (AI) continues to gain recognition globally, a recent survey outlines a comprehensive phased adoption strategy aimed at leveraging AI across various sectors. The strategy emphasizes the importance of institutional readiness, establishing common data standards, and initiating pilot projects that focus on low-cost AI applications, particularly in agriculture and public services.
In the immediate term, stakeholders are encouraged to prioritize foundational elements such as institutional readiness and standardization. This approach aims to streamline the integration of AI technologies within public services and agricultural practices, addressing both efficiency and accessibility. The pilot projects are intended to serve as test beds for innovative AI applications that could significantly reduce costs while enhancing service delivery and productivity.
Looking ahead, the survey indicates that public investment will shift toward bolstering domestic computing capacity and developing essential skills. This shift is crucial not only for fostering innovation but also for ensuring the safe deployment of AI technologies. By investing in skill development, governments can prepare their workforce to engage with AI, thereby maximizing its societal benefits while minimizing potential risks associated with its misuse.
The medium-term perspective highlights the necessity of establishing robust safety frameworks as AI becomes more integrated into various sectors. This proactive stance will help mitigate risks, ensuring that ethical considerations remain at the forefront of AI development. The focus on safety frameworks is particularly pertinent given the rapid advancements in AI capabilities, which necessitate a careful approach to governance and regulation.
The implications of this phased strategy extend beyond mere technological adoption; they represent a significant opportunity for economic growth and improved public services. By harnessing AI, countries can not only enhance agricultural productivity but also increase the efficiency of public sector operations. This dual focus is essential for addressing the challenges posed by growing populations and the increasing demand for sustainable agricultural practices.
As nations grapple with these transformative changes, international collaboration may play a pivotal role in shaping the future landscape of AI. Stakeholders from different sectors, including government, academia, and industry, must work together to share knowledge and best practices. Such collaboration could foster innovation while ensuring that the benefits of AI are equitably distributed.
In conclusion, the phased adoption strategy outlined in the survey reflects a thoughtful approach to integrating AI into society. As governments prepare for this transition, the emphasis on institutional readiness, skill development, and safety will be critical in navigating the complex landscape of AI technologies. This evolving narrative underscores the broader significance of AI not just as a technological advancement but as a driver for societal progress.
For more information on AI adoption strategies, visit OpenAI and Microsoft.
To understand the implications of AI in public services and agriculture, consider exploring resources from MIT and European Commission.