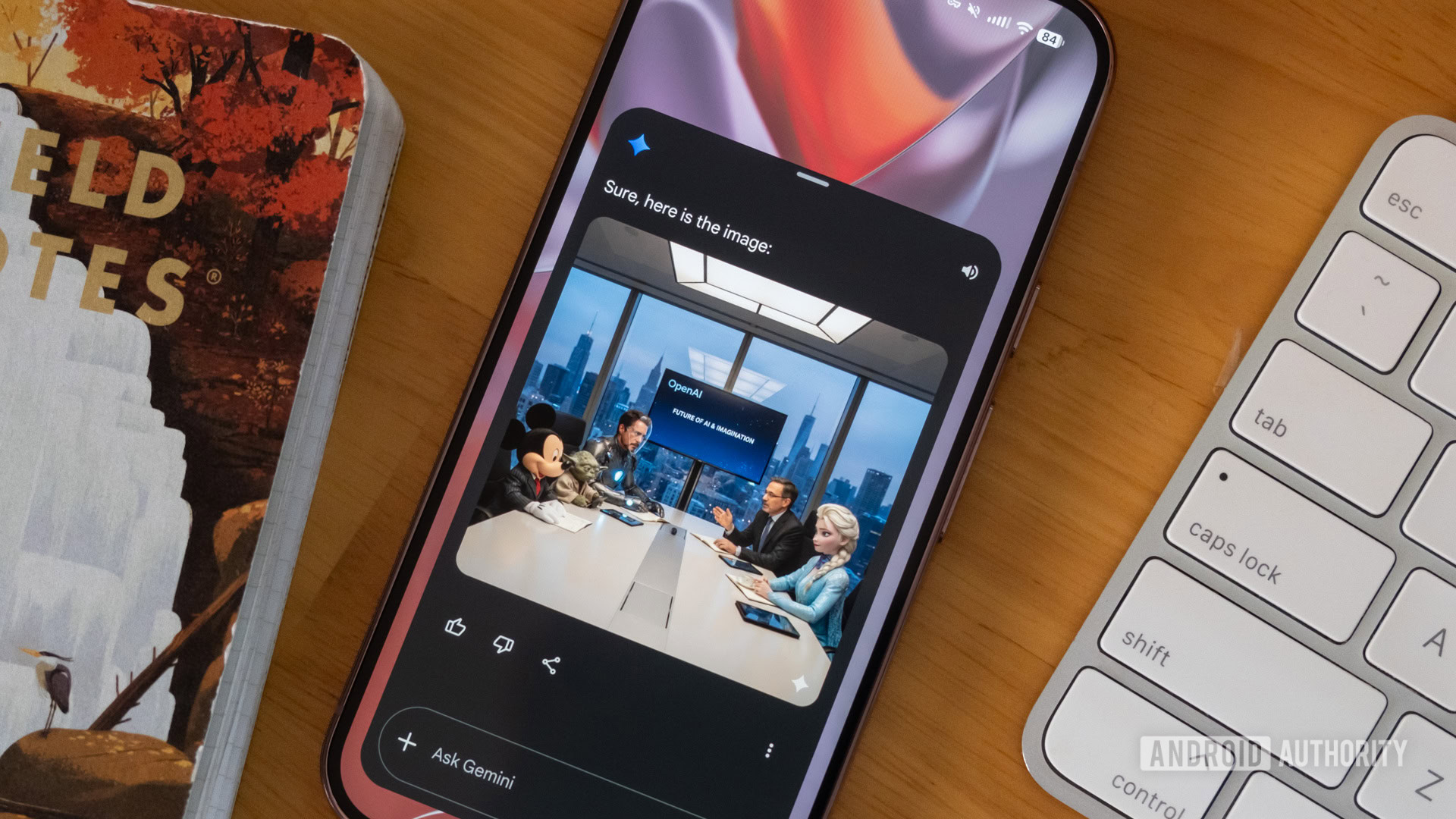
As the prevalence of generative AI technologies grows, concerns over the authenticity of images shared online are becoming increasingly significant. Taylor Kerns, a writer for Android Authority, recounted her experience relocating across the globe, where she heavily relied on platforms like Facebook Marketplace to find housing and other essentials. She noted that many of the images encountered during her search were digitally altered, often to the point of misrepresentation, complicating her decision-making process from afar. This phenomenon is not limited to one platform; AI-generated images and videos have rapidly spread across various online venues, contributing to the challenge of distinguishing real from synthetic content.
With tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Gemini becoming widely accessible, the risk of encountering misleading content has amplified. Kerns pointed out the challenges in detecting AI-generated imagery, particularly when it comes to human and animal representations. While landscapes may appear convincingly real, images featuring living beings often reveal uncanny characteristics. For instance, less advanced AI models frequently struggle with human anatomy, resulting in bizarre proportions or overlapping features. Furthermore, the depiction of skin and fur tends to be unnaturally smooth, lacking typical imperfections such as pores or wrinkles, which can signal artificial generation.
Beyond scrutinizing the main subject of an image, it is advisable to examine the surrounding elements. A case in point is an AI-generated image of singer Katy Perry, which appeared convincing at first glance. However, a closer inspection revealed multiple flaws in the background, including overlapping faces and disproportionate camera shapes, suggesting a lack of detail consistency. Such inconsistencies can be indicative of AI involvement, prompting viewers to dig deeper into an image’s authenticity.
For those skeptical about the veracity of a visual, performing a reverse image search can be a useful tool. Kerns highlighted that both Google and OpenAI have begun incorporating metadata into their AI-generated images, effectively acting as a watermark to identify their origins. Utilizing features like Google Lens can help users confirm whether an image is synthetic. Often, bad actors will employ low-quality images to obscure discrepancies, making reverse searches crucial for uncovering higher-quality versions and verifying the image’s source.
Another common feature of AI-generated images is the presence of garbled text, whether printed or handwritten. Kerns explained that while newer AI models have improved in generating text, the letters may still lack clarity. Observing the context of the text can also provide clues about authenticity; for example, an image purportedly from a foreign location that predominantly displays English might warrant further investigation. The nuances of a setting may be captured well, yet details like signage may expose inconsistencies.
Interestingly, while generative AI has advanced in creating realistic still images, its capabilities in producing video content remain less refined. Kerns noted that imperfections are more easily exposed in video due to the extended timeline, where interactions between objects and inconsistencies become evident. AI-generated videos often exhibit unrealistic movement, such as vehicles gliding on uneven surfaces, and struggle with accurately depicting shadows and reflections. Moreover, dialogue sync can be problematic, leading to rapid cuts that may raise suspicion about the video’s authenticity.
For those still finding it difficult to discern AI-generated content, seeking assistance from online communities can be beneficial. Platforms like Reddit feature dedicated threads where users analyze and discuss the authenticity of images and videos, providing a collective perspective. In some cases, Google’s Gemini chatbot can also assist by determining if an image has been generated by AI, checking for embedded watermarks and utilizing internal reasoning to assess authenticity.
As generative AI continues to evolve, the challenge of distinguishing real from synthetic content is likely to persist. While Kerns emphasized the importance of vigilance when assessing images online, she acknowledged the potential for even the most discerning viewers to be misled, especially when urgency clouds judgment. The increasing sophistication of AI-generated content underscores the necessity for robust verification practices, ensuring that users remain informed and cautious in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
See also Grok AI Under Fire: UK Regulators Investigate Explicit Deepfakes Amid User Misuse
Grok AI Under Fire: UK Regulators Investigate Explicit Deepfakes Amid User Misuse Smart Buildings Achieve 86% Energy Savings Using AI and Large Language Models
Smart Buildings Achieve 86% Energy Savings Using AI and Large Language Models Canva Hires Kshitiz Garg as Audio and Video Lead to Enhance Generative AI Research
Canva Hires Kshitiz Garg as Audio and Video Lead to Enhance Generative AI Research Disney+ Launches Vertical Video Feature for AI Native Generation, Integrates OpenAI Collaboration
Disney+ Launches Vertical Video Feature for AI Native Generation, Integrates OpenAI Collaboration Zhipu AI Debuts in Hong Kong, Surging 12.4% to $7.4B Market Cap as First LLM Public Company
Zhipu AI Debuts in Hong Kong, Surging 12.4% to $7.4B Market Cap as First LLM Public Company